Learn the basics of process design for biobased products. From feedstock to biomaterials, chemicals and biofuels.
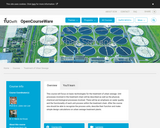
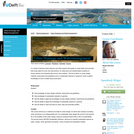
As fossil-based fuels and raw materials contribute to climate change, the use of renewable materials and energy as an alternative is in full swing. This transition is not a luxury, it is has become a necessity. We can use the unique properties of microorganisms to convert organic waste streams into biomaterials, chemicals and biofuels.
This course provides the insights and tools for biotechnological processes design in a sustainable way. Five experienced course leaders will teach you the basics of industrial biotechnology and how to apply these to the design of fermentation processes for the production of fuels, chemicals and foodstuffs. Throughout the course, you will be challenged to design your own biotechnological sprocess and evaluate its performance and sustainability. The undergraduate course includes guest lectures from industry as well as from the University of Campinas in Brazil, with over 40 years of experience in bio-ethanol production. The course was a MOOC in a joint initiative of TU Delft, the international BE-Basic consortium and University of Campinas.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Engineering
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Delft University of Technology
- Provider Set:
- TU Delft OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Prof.dr. Isabel Arends
- Prof.dr.ir. Henk Noorman
- Prof.dr.ir. Luuk van der Wielen
- Prof.dr.ir. Sef Heijnen
- Date Added:
- 08/20/2018