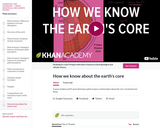
S-wave shadow and P-wave detection patterns give us information about the core. Created by Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Astronomy
- Physical Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 02/04/2011


S-wave shadow and P-wave detection patterns give us information about the core. Created by Sal Khan.
A presentation of some Hubble Image of Galaxies. Created by Sal Khan.
Hubble's Law. Created by Sal Khan.
From the extinction of the dinosaurs to humanity. Created by Sal Khan.
The students will learn about recent meteor strikes and the effects they can have. They will then examine their significance in the history of the planet, and what they do to the surface of a planet when forming a crater. The students will then experimentally determine how the size and impact velocity of a meteorite determine the size of the crater.

An introduction to Intergalactic Scale. Created by Sal Khan.
Light and the electromagnetic radiation spectrum. Wave and particle-like behavior, and how to calculate the wavelength or frequency of a light wave. Created by Sal Khan.
The Moon and the sun look roughly the same size in the sky because although the sun’s diameter is ~400 times greater than the Moon’s, the sun is ~400 times farther away from the Earth as the Moon is! The Moon goes through phases because as it rotates around the Earth, different parts of the Moon are made visible to us from the sun’s light. Created by Sal Khan.
Working through a calculation for K-Ar dating (good to have some prior experience with e and logarithms). Created by Sal Khan.
Lifecycle of Massive Stars. Created by Sal Khan.

Students groups act as aerospace engineering teams competing to create linear equations to guide space shuttles safely through obstacles generated by a modeling game in level-based rounds. Each round provides a different configuration of the obstacle, which consists of two "gates." The obstacles are presented as asteroids or comets, and the linear equations as inputs into autopilot on board the shuttle. The winning group is the one that first generates the successful equations for all levels. The game is created via the programming software MATLAB, available as a free 30-day trial. The activity helps students make the connection between graphs and the real world. In this activity, they can see the path of a space shuttle modeled by a linear equation, as if they were looking from above.
Students will experimentally learn how meteoroids are formed. They will melt a comet, learning about its composition, and break apart asteroids. The students learn the differences between meteoroids, meteors and meteorites and how the impact of asteroids/meteoroids can affect life on Earth.
How changes in Earth's rotation can effect Earth's seasons and climate. Created by Sal Khan.

Students are introduced to the futuristic concept of the moon as a place people can inhabit. They brainstorm what people would need to live on the moon and then design a fantastic Moon colony and decide how to power it. Students use the engineering design process, which includes researching various types of energy sources and evaluating which would be best for their moon colonies.
For thousands of years, navigators have looked to the sky for direction. Today, celestial navigation has simply switched from using natural objects to human-created satellites. A constellation of satellites, called the Global Positioning System, and hand-held receivers allow for very accurate navigation. In this lesson, students investigate the fundamental concepts of GPS technology trilateration and using the speed of light to calculate distances.

This lesson unit provides an insight into the navigational methods of the Bronze Age Mediterranean peoples. The students explore the link between history and astronomical knowledge. Besides an overview of ancient seafaring in the Mediterranean, the students use activities to explore early navigational skills using the stars and constellations and their apparent nightly movement across the sky. In the course of the activities, they become familiar with the stellar constellations and how they are distributed across the northern and southern sky.

Students learn how engineers navigate satellites in orbit around the Earth and on their way to other planets in the solar system. In accompanying activities, they explore how ground-based tracking and onboard measurements are performed. Also provided is an overview of orbits and spacecraft trajectories from Earth to other planets, and how spacecraft are tracked from the ground using the Deep Space Network (DSN). DSN measurements are the primary means for navigating unmanned vehicles in space. Onboard spacecraft instruments might include optical sensors and an inertial measurement unit (IMU).

Lets us look over the shoulders of scientists and glimpse the often-unseen moments of investigation. Take virtual field trips to eight observatories -- Arecibo, where astrobiologists search for signs of life beyond the solar system; Las Cuevas, a research station in Central America's largest remaining rainforest; and others. See interviews, photos, and broadcasts that explore the origins of matter, the universe, and life itself.
Ozone layer and eukaryotes show up in the Proterozoic eon. Great oxygenation event (oxygen catastrophe). Created by Sal Khan.
Pangaea - the idea of Pangaea and some of the evidence behind it. Created by Sal Khan.