Advice from storytellers on structure.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Arts and Humanities
- Computer Science
- Graphic Arts
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Pixar
- Author:
- Disney Pixar
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 07/14/2021


Advice from storytellers on structure.
Advice from our storytellers.
How to combine data from a database using SQL.
Thinking about how we get Calories from the land limits human population densities. Created by Sal Khan.
How long of a runway does an A380 need? Created by Sal Khan.
Figuring how long it takes an A380 to take off given a constant acceleration. Created by Sal Khan.

Alcohol or ethanol fermentation, including yeast and its role in bread and wine production.
How can we improve the speed of a (deterministic) primality test? Created by Brit Cruise.
The properties of organic molecules depend on the structure, and knowing the names of organic compounds allow us to communicate with other chemists. We'll be learning about different aspects of molecular structure, including common functional groups and conformations.

Allele frequencies in populations and how they differ from genotype frequencies. Created by Sal Khan.

A gene as a stretch of DNA on a chromosome. Alleles as versions (sequence variants) of a gene.
An overview of altering tables after creation

An example of simplifying a seemingly complicated resistor circuit. Created by Willy McAllister.
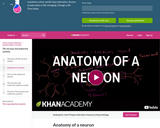
Neurons (or nerve cells) are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neurons are composed of three main parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Signals are received through the dendrites, travel to the cell body, and continue down the axon until they reach the synapse (the communication point between two neurons).

Understanding the structure of a skeletal muscle cell.. Created by Raja Narayan.
Introducing angular momentum conceptually starting from linear momentum. Also covers some real-life examples. Created by Sal Khan.

David explains the meaning of angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration. Created by David SantoPietro.
In uniform circular motion, angular velocity (𝒘) is a vector quantity and is equal to the angular displacement (Δ𝚹, a vector quantity) divided by the change in time (Δ𝐭). Speed is equal to the arc length traveled (S) divided by the change in time (Δ𝐭), which is also equal to |𝒘|R. And arc length (S) is equal to the absolute value of the angular displacement (|Δ𝚹|) times the radius (R).

An introduction to how animals communicate.

Introduction to foraging (animal behavior).