
This diagram of Hawaii's Kilauea volcano shows the underground "plumbing" and paths of magma.
- Subject:
- Physical Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Author:
- National Air and Space Museum
- Date Added:
- 06/15/2022


This diagram of Hawaii's Kilauea volcano shows the underground "plumbing" and paths of magma.
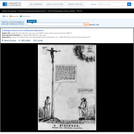
Entered according to Act of Congress in the year 1837, by H.R. Robinson, in the Clerk's Office of the District Court of the United States of the Southern District of New York. Printed & published by H.R. Robinson, 52 Cortlandt Street, New York.|Title appears as it is written on the item.|Forms part of: American cartoon print filing series (Library of Congress)

This online tool enables students to learn about and write diamante poems.
This lesson is for an AP Language and Compositon course and is focused on developing precision of language and tone in a student's writing. It is the beginning of a process that will as students to be more purposeful with language.
In this segment from Curious, learn about creating energy from solar rays to meet the growing energy needs of the world.
The digestive system is amazing: it takes the foods we eat and breaks them into smaller components that our body can use for energy, cell repair and growth. This lesson introduces students to the main parts of the digestive system and how they interact. In addition, students learn about some of the challenges astronauts face when trying to eat in outer space.

Students explore multiple forms of digital etiquette and citizenship. They research current events based around digital concerns and innovations. Eventually, they apply that knowledge to their own lives and use of technology to develop 5 top guidelines for digital device usage for their peers. Students share their presentations and projects in an exhibit-style venue. Using a survey, students vote for their top choices, eventually selecting one choice to implement.Standards:CCSS English Language Arts (Grade 8)Ohio Standards for Technology

In this problem-based learning module, students will investigate why is it important that students be careful what is posted for everyone to see. Students will investigate and discuss these questions during this module that directly relate to their daily life. Students will work cooperatively in groups to design an infomercial to be presented to elementary students and/or parents and community members. Key Learning Targets: I can use technology to produce and publish my work, and link to sources.I can include multimedia projects or visual displays when they will be helpful in clarifying and emphasizing information.I can actively participate and contribute to a discussion with my teacher and my peers. I can present my findings to a group or audience in a clear and concise way.I can create a storyboard to prepare a public service announcement. I can compare contrast trends of technology. I can write an explanatory paragraph to examine a topic (present and future digital footprint).

This resource provides a description and links to the original materials for a multi-day unit created by teacher-librarians at Highline Public Schools. The unit shows 9th grade students how to access, analyze, evaluate, and cite information sources.

This resource provides a description and links to the original materials for a multi-day unit created by teacher-librarians at Highline Public Schools. The unit shows 9th grade students how to access, analyze, evaluate, and cite information sources.

Striking images can leave lasting impressions on viewers. In this lesson, students make text-self-world connections to a nature- or science-related topic as they collaboratively design a multimedia presentation.

In this unit students will reflect on their own media environment, understand how cognitive bias and social media algorithms influence that environment, and learn how to investigate new sources and claims online. These activities culminate in a student-led "social science fair" MisinfoNight event where they present their new skills and knowledge to family members to help them become more savvy information consumers.
The information revolution of the 21st century is as significant and transformative as the industrial revolution of the 19th century. In this unit, students – and by proxy their families – will learn about the challenges of our current information landscape and how to navigate them. This unit is split into four modules. These modules can be done sequentially or stand on their own, depending on students’ needs and teachers’ timeframes. In this module (1 of 4), students analyze their own use of online social media platforms and learn how filter bubbles and confirmation bias shape the content of their media environment.




Learn about Greek gods, heroes, and creatures through digital storytelling produced by students who have learned research techniques.

So many dinosaurs have names that come from Greek or Latin roots. This activity lets kids explore those affixes.
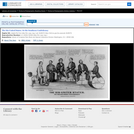
The Confederate leaders are portrayed as a band of competing opportunists led by South Carolina governor and secessionist Francis Pickens (far left). The artist criticizes the January 1861 secession of five states from the lower South, following the lead of South Carolina, which had formally declared its independence a month before. Armed with a whip and a pistol, Pickens sits on the back of a young slave, pronouncing, "South Carolina claims to be file leader and general whipper in of the new Confederacy, a special edict! Obey and tremble!" The other leaders are also armed. Pickens's tyranny is met by expressions of self-interest from the other confederates. The nature of these individual interests are conveyed pictorially and in the text. Leaders from Alabama, Mississippi, and Georgia sit on bales of cotton, while Florida and Louisiana sit on a wrecked ship's hull and a barrel of sugar respectively. Florida (represented by a bearded man, possibly Stephen R. Mallory, senator and later secretary of the Confederate navy ): "We want it distinctly understood that all the lights on the Coast will be put out, in order to facilitate wrecking business." Alabama (William L. Yancey): "Alabama proclaims that CĚ_Ąotton is King,' and the rest of the Confederacy "must obey" that Sovereign. Mississippi (Jefferson Davis): "We came in, with the understanding that we shall issue bonds to an unlimited extent, with our ancient right of repudiation when they became due." Georgia (Governor Joseph E. Brown): "Georgia must have half the honors, and all the profits, or back she goes to old Pluribus Unum.'" Louisiana (a mustachioed man): "A heavy duty must be levied on foreign sweetening in order to make up for what we have sacrificed in leaving the Union, otherwise we shall be like a PĚ_Ąelican in the wilderness!'" Although Texas, which seceded on February 1, is not represented here, the print probably appeared at the time of the Montgomery convention in early February when the Confederate States of America was formed, but before Jefferson Davis assumed its presidency. Texas did not attend that convention.|Published by Currier & Ives, 152 Nassau St. N.Y.|Title appears as it is written on the item.|Gale, no. 1730.|Weitenkampf, p. 128.|Published in: American political prints, 1766-1876 / Bernard F. Reilly. Boston : G.K. Hall, 1991, entry 1861-6.
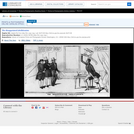
Three men at left, one saying, "Verily friend Darg since we have returned thee thy money, I claim the reward of $1000 - Brother Barney Corse was merely my agent, verily!" Another "Yea verily I was but thy instrument Brother Hopper as Brother Ruggles here knoweth!" Man at right, brandishing chair and holding bag marked $6908, rails at their impudence and tells them to "get out of the house."|Copyright by H.R. Robinson.|Title appears as it is written on the item.|Forms part of: American cartoon print filing series (Library of Congress)