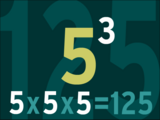
Students will evaluate numerical expressions with whole-number exponents.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Author:
- April Hamma
- Date Added:
- 06/09/2022
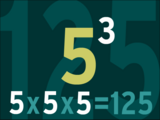
Students will evaluate numerical expressions with whole-number exponents.

This task was developed by high school and postsecondary mathematics and health sciences educators, and validated by content experts in the Common Core State Standards in mathematics and the National Career Clusters Knowledge & Skills Statements. It was developed with the purpose of demonstrating how the Common Core and CTE Knowledge & Skills Statements can be integrated into classroom learning - and to provide classroom teachers with a truly authentic task for either mathematics or CTE courses.
This unit is an EQuIP Exemplar for adult education (http://achieve.org/equip). Students will connect their prior, real-world knowledge to the concept of order in mathematics. They will go through a discovery process with content that will build a deep, conceptual understanding of the properties of operations to explain why we perform operations in a certain order when we see just the naked numbers.

This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to: Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole-number exponents, recognizing and applying the conventional order of operations; Write and evaluate numerical expressions from diagrammatic representations and be able to identify equivalent expressions; apply the distributive and commutative properties appropriately; and use the method for finding areas of compound rectangles.
Students watch video clips from the October Sky and Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone movies to see examples of projectile motion. Then they explore the relationships between displacement, velocity and acceleration, and calculate simple projectile motion. The objective of this activity is to articulate concepts related to force and motion through direct immersive interaction based on "The Science Behind Harry Potter" theme. Students' interest is piqued by the use of popular culture in the classroom.


Expressions
Type of Unit: Concept
Prior Knowledge
Students should be able to:
Write and evaluate simple expressions that record calculations with numbers.
Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
Interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them.
Lesson Flow
Students learn to write and evaluate numerical expressions involving the four basic arithmetic operations and whole-number exponents. In specific contexts, they create and interpret numerical expressions and evaluate them. Then students move on to algebraic expressions, in which letters stand for numbers. In specific contexts, students simplify algebraic expressions and evaluate them for given values of the variables. Students learn about and use the vocabulary of algebraic expressions. Then they identify equivalent expressions and apply properties of operations, such as the distributive property, to generate equivalent expressions. Finally, students use geometric models to explore greatest common factors and least common multiples.

Students critique the work of other students and revise their own work based on feedback from the teacher and peers.Key ConceptsConcepts from previous lessons are integrated into this unit task: rewriting expressions, using parentheses, and using the distributive property. Students apply their knowledge, review their work, and make revisions based on feedback from you and their peers. This process creates a deeper understanding of the concepts.Goals and Learning ObjectivesApply knowledge of expressions to correct the work of other students.Track and review the choice of strategy when problem solving.

Students express the lengths of trains as algebraic expressions and then substitute numbers for letters to find the actual lengths of the trains.Key ConceptsAn algebraic expression can be written to represent a problem situation. More than one algebraic expression may represent the same problem situation. These algebraic expressions have the same value and are equivalent.To evaluate an algebraic expression, a specific value for each variable is substituted in the expression, and then all the calculations are completed using the order of operations to get a single value.Goals and Learning ObjectivesEvaluate expressions for the given values of the variables.

Students represent problem situations using expressions and then evaluate the expressions for the given values of the variables.Key ConceptsAn algebraic expression can be written to represent a problem situation.To evaluate an algebraic expression, a specific value for each variable is substituted in the expression, and then all the calculations are completed using the order of operations to get a single value.Goals and Learning ObjectivesDevelop fluency in writing expressions to represent situations and in evaluating the expressions for given values.

Students are introduced to classroom routines and expectations, and complete a full mathematics lesson. The class discusses how to clearly present work to classmates. Partner work is modeled, and partners then work to match numerical expressions to corresponding word descriptions. Students read and discuss a summary of the math in the lesson, and then write a reflection about their thoughts.Key ConceptsStudents match a numerical expression to its corresponding description in words. Students interpret parentheses and brackets in numerical expressions and they construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students learn to use the exponent 2 to represent squaring.Goals and Learning ObjectivesDescribe the classroom routines and expectations.Consider how to present work clearly to classmates.Collaborate with a partner.Critique a partner’s reasoning.Connect a numerical expression to its corresponding word description.Learn to use an exponent of 2 to represent squaring.

6th Grade Chapter 5: Geometry - Parent Workbook

Students are introduced to the field of biomechanics and how the muscular system produces human movement. They learn the importance of the muscular system in our daily lives, why it is important to be able to repair muscular system injuries and how engineering can help.

This supplemental resource provides problems and activities related to Patterns, Relationships and Functions in Middle School Mathematics.

The purpose of this task is to ask students to write expressions and to consider what it means for two expressions to be equivalent.
Khan Academy Video Tutorial. Introduction to basic algebraic equations of the form Ax=B

This problem asks the student to evaluate three numerical expressions that contain the same integers yet have differing results due to placement of parentheses.
Investigating a waterwheel illustrates to students the physical properties of energy. They learn that the concept of work, force acting over a distance, differs from power, which is defined as force acting over a distance over some period of time. Students create a model waterwheel and use it to calculate the amount of power produced and work done.