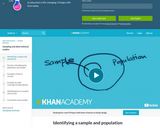
Short video which describes the difference between a sample and a population.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 12/29/2017

Short video which describes the difference between a sample and a population.

Introduction to Sociology 2e adheres to the scope and sequence of a typical, one-semester introductory sociology course. It offers comprehensive coverage of core concepts, foundational scholars, and emerging theories, which are supported by a wealth of engaging learning materials. The textbook presents detailed section reviews with rich questions, discussions that help students apply their knowledge, and features that draw learners into the discipline in meaningful ways. The second edition retains the book’s conceptual organization, aligning to most courses, and has been significantly updated to reflect the latest research and provide examples most relevant to today’s students. In order to help instructors transition to the revised version, the 2e changes are described within the preface.

Differentiate between four kinds of research methods: surveys, field research, experiments, and secondary data analysisUnderstand why different topics are better suited to different research approaches

An introduction and examples of how to use basic concepts in statistics, used in quantative studies: samples, population, variables, random samples, groups, ranking, measurement levels.

Use data from multiple samples to draw inferences about a population and investigate variability in estimates of the characteristic of interest.

Students learn about one method used in environmental site assessments. They practice soil sampling by creating soil cores, studying soil profiles and characterizing soil profiles in borehole logs. They use their analysis to make predictions about what is going on in the soil and what it might mean to an engineer developing the area.
This 11-minute video lesson shows how to use the variance of a sample to estimate the variance of a population. [Statistics playlist: Lesson 14 of 85]

Students use DNA profiling to determine who robbed a bank. After they learn how the FBI's Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) is used to match crime scene DNA with tissue sample DNA, students use CODIS principles and sample DNA fragments to determine which of three suspects matches evidence obtain at a crime location. They communicate their results as if they were biomedical engineers reporting to a police crime scene investigation.