
Data should not be entered with higher precision than they were collected in.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Information Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- DataONE
- Date Added:
- 03/28/2022

Data should not be entered with higher precision than they were collected in.

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.

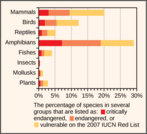
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify new technologies for describing biodiversityExplain the legislative framework for conservationDescribe principles and challenges of conservation preserve designIdentify examples of the effects of habitat restorationDiscuss the role of zoos in biodiversity conservation

A Digital Project Preservation Plan is designed to help with organizing preservation efforts for digital projects. Initially drafted as a companion guide meant to fill the gap on best methods for preserving digital scholarship or digital humanities projects, it can also be applied to digital projects outside the humanities. This preservation plan is most beneficial to those digital humanities (DH) project creators who need guidance on how to start a digital project with preservation in mind. Although the DH community has shared resources and case studies, the examples available tend to focus on DH development, and less on DH preservation. These resources are also located in disparate locations. The Digital Project Preservation Plan is a singular guide, focusing on DH preservation, as a starting point with references to more resources and related DH practices. This is a working document, available to practitioners in whole or part; ideally, it will be used in the early stages of project planning and consulted and revised regularly. The preservation infrastructure should be designed and built as a collaborative effort from the beginning of the project. As priorities, methods and technologies change, the preservation plan will need to be updated and modified accordingly.
This book has been used in humanities (history) and media courses but is applicable to any course that has digital/web project components.
The Table of Contents for this publication includes:
Summary, Project Charter, Digital File Inventory, Additional Considerations, Preservation Plan-A Summary and Checklist, References/Plan Resources, Appendix A: Project Charter, Appendix B: Digital File Inventory, Appendix C: Project Profile, Appendix D: Collaborators Web Publishing Agreement, Appendix E: Universal Design Checklist, Appendix F: Preservation Guidance Checklist, and the Glossary.

This video resource is presented as a real-world application of chemistry in the field of archaeology. Conservator, Nichole Doub, walks through the process of electrolytic reduction and how it is used to conserve archaeologically recovered artifacts. Use to support Maryland/NGSS for grades 5, MS, and HS. For 5-PS1-1, pair with the Exploratorium's "Copper Caper" activity for a similar reaction which can be conducted safely in the classroom--have students watch the video and discuss why the spoon formed tarnish and why the tarnish was not visible as particles moved from the spoon to the sacrificial anode. For MS-PS1-1, pair with the Exploratorium's "Indicating Electrolysis" activity and have the students explain the charges of oxygen/hydrogen and compare/contrast those with the silver and sulfur in the tarnish. Have students research silver sulfide (the usual tarnish found on silver artifacts) and model a single molecule of it before and after electrolysis. For HS-PS1-1 have students research silver sulfide and model a molecule of it prior to watching the video and predict what will happen when the positive or negative charges change. For HS-PS2-6, have students postulate why, historically, coins were made from silver and gold (with reference to their chemical reactions), then have students design a coin and specify a different metal to make it out of, explaining why the atomic properties of that metal make it appropriate for use in currency. If you evaluate or use this resource, consider responding to this short (4 question) survey at bit.ly/3G0bNqy
This collection uses primary sources to environmental preservation in the Progressive Era. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.

When the first edition of Folklife and Fieldwork was published in 1979 there were only a handful of professional state folklorists. Today nearly every state has a program for documenting and presenting its own folk cultural heritage. Folklife fieldwork has gone beyond its early missions of preservation and scholarship to serve new uses, such as providing information to economists, environmentalists, and community planners. New technologies for preserving and presenting traditional cultural expression have been developed. A new generation of professionally trained folklorists have emerged from university programs, and many now work in state and local organizations to sponsor concerts, Web site presentations, exhibits, and other cultural heritage programs. But regardless of the number of folklorists available for professional projects or the sophistication of the technology, there is still a need for the participation of all citizens in the process of documenting our diverse traditional culture. First Edition Prepared 1979 by Peter Bartis; Revised 2002.

In this class, food serves as both the subject and the object of historical analysis. As a subject, food has been transformed over the last 100 years, largely as a result of ever more elaborate scientific and technological innovations. From a need to preserve surplus foods for leaner times grew an elaborate array of techniques – drying, freezing, canning, salting, etc – that changed not only what people ate, but how far they could/had to travel, the space in which they lived, their relations with neighbors and relatives, and most of all, their place in the economic order of things. The role of capitalism in supporting and extending food preservation and development was fundamental. As an object, food offers us a way into cultural, political, economic, and techno-scientific history. Long ignored by historians of science and technology, food offers a rich source for exploring, e.g., the creation and maintenance of mass-production techniques, industrial farming initiatives, the politics of consumption, vertical integration of business firms, globalization, changing race and gender identities, labor movements, and so forth. How is food different in these contexts, from other sorts of industrial goods? What does the trip from farm to table tell us about American culture and history?

This course will explore food in modern American history as a story of industrialization and globalization. Lectures, readings, and discussions will emphasize the historical dimensions of—and debates about—slave plantations and factory farm labor; industrial processing and technologies of food preservation; the political economy and ecology of global commodity chains; the vagaries of nutritional science; food restrictions and reform movements; food surpluses and famines; cooking traditions and innovations; the emergence of restaurants, supermarkets, fast food, and slow food. The core concern of the course will be to understand the increasingly pervasive influence of the American model of food production and consumption patterns.

Sara Rivers-Cofield, Curator of Federal Collections at the Maryland Archaeological Conservation Laboratory, walks through applying acid-free paper labels to artifacts. This is an alternative to labelling artifacts with permanent archival ink, and the tutorial is appropriate for both students and professional education. The Maryland Archaeological Conservation Laboratory (MAC Lab) standards and guidelines for preparing artifact collections and their associated records, both paper and digital, for permanent curation at the lab can be found at https://jefpat.maryland.gov/Documents/mac-lab/technical-update-no1-collections-and-conservation-standards.pdf
The MAC Lab is a state-of-the-art archaeological research, conservation, and curation facility located at Jefferson Patterson Park and Museum, the State Museum of Archaeology. The MAC Lab serves as the primary repository for archaeological collections recovered from land-based and underwater projects conducted by state and federal agencies throughout Maryland.
This resource is part of Jefferson Patterson Park and Museum’s open educational resources project to provide history, ecology, archaeology, and conservation resources related to our 560 acre public park. JPPM is a part of the Maryland Historical Trust under the Maryland Department of Planning.

Walk through how to pack artifacts in bags and boxes for curation and storage with Sara Rivers-Cofield, Curator of Federal Collections, and Alice Merkel, Collections Assistant, at the Maryland Archaeological Conservation Laboratory. In addition, tips are offered as to how best to arrange boxes to simplify handling and, as always, best protect artifacts. The Maryland Archaeological Conservation Laboratory (MAC Lab) standards and guidelines for preparing artifact collections and their associated records, for permanent curation at the lab can be found at https://jefpat.maryland.gov/Documents/mac-lab/technical-update-no1-collections-and-conservation-standards.pdf
The MAC Lab is a state-of-the-art archaeological research, conservation, and curation facility located at Jefferson Patterson Park and Museum, the State Museum of Archaeology. The MAC Lab serves as the primary repository for archaeological collections recovered from land-based and underwater projects conducted by state and federal agencies throughout Maryland.
This resource is part of Jefferson Patterson Park and Museum’s open educational resources project to provide history, ecology, archaeology, and conservation resources related to our 560 acre public park. JPPM is a part of the Maryland Historical Trust under the Maryland Department of Planning.

Art tells the story of humanity across societies and cultures, but keeping that art around for future generations can be a monumental task. In this episode of Crash Course Art History, we’ll learn how art historians preserve, restore, and conserve art that tells the story of who we are and who we want to be.
Chapters:
Introduction: "The Last Supper"
Preservation
Restoration
"Ecce Homo"
Conservation
Review & Credits
Credits

This lesson will introduce students to environmental issues. Students will recognize environmental opinions and perspective, which will help them define themselves and others as either preservationists or conservationists. Students also learn about the importance of teamwork in engineering.

This class is designed to provide the student with a global to molecular-level perspective of organic matter cycling in the oceans and marine sediments. Topics include: Organic matter (C,N,P) composition, reactivity and budgets within, and fluxes through, major ocean reservoirs; microbial recycling pathways for organic matter; models of organic matter degradation and preservation; role of anoxia in organic matter burial; relationships between dissolved and particulate (sinking and suspended) organic matter; methods for characterization of sedimentary organic matter; and application of biological markers as tools in oceanography. Both structural and isotopic aspects are covered.
Students in grade two explore the lives of actual people who make a difference in their everyday lives. They differentiate between events that happened long ago and events that happened yesterday by studying their family histories. A number of projects are completed that preserve the past, capture the present, or impact the future, including analyzing information and drawing conclusions about how and why the world has changed. The unit concludes with students creating family history time capsules that preserve the past and present for the future.
This unit plan was originally developed by the Intel® Teach program as an exemplary unit plan demonstrating some of the best attributes of teaching with technology.

The New England Collaborative Data Management Curriculum (NECDMC) project is led by the Lamar Soutter Library at the University of Massachusetts Medical School in partnership with several libraries in the New England region.
NECDMC is an instructional tool for teaching data management best practices to undergraduates, graduate students, and researchers in the health sciences, sciences, and engineering disciplines. Each of the curriculum’s seven online instructional modules aligns with the National Science Foundation’s data management plan recommendations and addresses universal data management challenges. Included in the curriculum is a collection of actual research cases that provides a discipline specific context to the content of the instructional modules. These cases come from a range of research settings such as clinical research, biomedical labs, an engineering project, and a qualitative behavioral health study. Additional research cases will be added to the collection on an ongoing basis. Each of the modules can be taught as a stand-alone class or as part of a series of classes. Instructors are welcome to customize the content of the instructional modules to meet the learning needs of their students and the policies and resources at their institutions

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"In recent years, the study of microbial communities has greatly benefitted from advances in both genetic sequencing and more traditional culture-based approaches, unlocking their potential to drive the development of new medical treatments like never before, but the techniques used for sample preservation could affect which microbes are ultimately cultured and thus constrain the discovery of previously undescribed species and microbial functions. To better understand how preservation affects the study of anaerobic bacteria in the gut, researchers froze human fecal samples at -80°C after adding Cary-Blair medium with or without 20% glycerol or 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to some of them. These preservatives are often used when transporting and freezing fecal and other clinical specimens. They found that the preservation conditions affected the number of bacterial anaerobes cultured from the samples, as well as the recovery of particular genera..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
The purpose of Preservation Problem Solvers is to encourage students to use leadership and resourceful behaviors to think like a scientist. This module extends the Essential Strategies of Attributes, Questioning, and Creative Problem Solving introduced in Kindergarten and First Grade, is for all students. The classroom teacher should work with a specialist or special educator to find or develop alternate activities or resources for visually impaired students, where appropriate.