27 Results

This module introduces the concept of biological absorption, storage and distribution of chemicals.
- Subject:
- Astronomy
- Education
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Space Science
- Material Type:
- Interactive
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- UCAR Staff
- Provider Set:
- Visionlearning
- Author:
- Morris Zedeck
- Date Added:
- 01/29/2004

Students compare and contrast passive and active transport by playing a game to model this phenomenon. Movement through cell membranes is also modeled, as well as the structure and movement typical of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Concentration gradient, sizes, shapes and polarity of molecules determine the method of movement through cell membranes. This activity is associated with the Test your Mettle phase of the legacy cycle.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Applied Science
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Melinda M. Higgins
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

Students color-code a schematic of a cell and its cell membrane structures. Then they complete the "Build-a-Membrane" activity found at http://learn.genetics.utah.edu. This reinforces their understanding of the structure and function of animal cells, and shows them the importance of being able to construct a tangible model of something that is otherwise difficult to see.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Amber Spolarich
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

Worksheet that goes over the types of transport associated with a cell membrane.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Homework/Assignment
- Author:
- Lisa Zung
- Date Added:
- 07/02/2020
This interactive feature describes some of the most important structures and functions of the cell membrane.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Interactive
- Provider:
- PBS LearningMedia
- Provider Set:
- PBS Learning Media: Multimedia Resources for the Classroom and Professional Development
- Author:
- National Science Foundation
- WGBH Educational Foundation
- Date Added:
- 09/26/2003

Students learn about the different structures that comprise cell membranes, fulfilling part of the Research and Revise stages of the legacy cycle. They view online animations of cell membrane dynamics (links provided). Then they observe three teacher demonstrations that illustrate diffusion and osmosis concepts, as well as the effect of movement through a semi-permeable membrane using Lugol's solution.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Amber Spolarich
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

This is a video and supporting worksheet covering membrane transport processes (Chapter 3).
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Biology
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Author:
- Valerie Pennington (Penguin Prof)
- Date Added:
- 03/04/2024

Learn about how phospholipids form the cell membrane, and what types of molecules can passively diffuse thorugh the membrane. By William Tsai. . Created by William Tsai.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 09/17/2013

Learn about the major components that make up our cell membrane and the fluid mosaic model. By William Tsai.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 09/17/2013
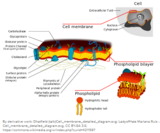
In this seminar you will create images of the biologically important structures of the cell membrane. The pictures will be translated to function. You will practice the terminology of these structures to associate their importance in the function of the cell membrane. The inquiry lab will allow you to design a model of the limitations of cell growth due to the cell membrane using water balloons.StandardsBIO.A.2.2.3 Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in organisms.BIO.A.4.2.1 Explain how organisms maintain homeostasis (e.g., thermoregulation, water regulation, oxygen regulation).BIO.A.4.1.3 Describe how endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and other membrane-bound cellular organelles facilitate transport of materials within cells.BIO.A.4.1.2 Compare and contrast the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane (i.e., passive transport -- diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion; active transport -- pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis).BIO.A.4.1.1 Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Author:
- Bonnie Waltz
- Deanna Mayers
- Tracy Rains
- Date Added:
- 10/07/2017
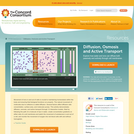
Movement of ions in and out of cells is crucial to maintaining homeostasis within the body and ensuring that biological functions run properly. The natural movement of molecules due to collisions is called diffusion. Several factors affect diffusion rate: concentration, surface area, and molecular pumps. This activity demonstrates diffusion, osmosis, and active transport through 12 interactive models.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Material Type:
- Data Set
- Lecture Notes
- Simulation
- Provider:
- Concord Consortium
- Provider Set:
- Concord Consortium Collection
- Author:
- The Concord Consortium
- Date Added:
- 01/13/2012
Hank tells us about the city of Eukaryopolis - the animal cell that is responsible for all the cool things that happen in our bodies.
Chapters:
1) Robert Hooke
2) Cilia/Flagella
3) Cell Membrane
4) Cytoplasm/Cytoskeleton/Centrosomes
5) Endoplasmic Reticulum
6) Ribosomes
7) Golgi Apparatus
8) Lysosomes
9) Nucleus
10) Mitochondria
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Complexly
- Provider Set:
- Crash Course Biology (2012)
- Date Added:
- 02/20/2012
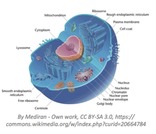
Eukaryotic cells are the foundation of our human body. They help us produce energy, grow, move, and carry out all our life functions. Looking at these cells, the learner will be challenged to explain how they help us grow and function. Eukaryotic cells are unique in the cellular world because they have membrane bound organelles. For this lesson experience, the learner will explore eukaryotic cell structure and function. Additionally they will travel through models of the cells, drawing comparisons with life functions at the micro and macro level.StandardsBIO.A.1.2.1 Compare cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Author:
- Bonnie Waltz
- Deanna Mayers
- Tracy Rains
- Date Added:
- 10/01/2017

This text been designed for an undergraduate human anatomy and physiology course at a medium sized public university. This text has been modified from the original OpenStax text to encourage more active reading for an early undergraduate student taking the first semester of a year-long human anatomy and physiology course sequence. This text has been targeted to our student population, consisting primarily of first semester pre-nursing and kinesiology majors at a university with a high proportion of first generation and PELL-eligible students who benefit from lower barriers to entry into the field. Therefore, freely-available and differently presented text can be beneficial to this student population. This version was designed with the intention of distributing it section by section through a learning management system. If this mode of distribution is used, connection to an assessment tool could be utilized. Systems covered include skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous.
As this text reorganizes and modifies an OpenStax’s Anatomy and Physiology 2e (see related resources link below), chapter numbers and chapter section numbers from the original have been preserved in this document. Material supplemented from other sources is cited within the text.
Course connections: Undergraduate courses aimed towards freshmen or sophomore, including Anatomy and Physiology, Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology, Physiology, Introduction to Physiology, Human Biology or similar with a human focus.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Textbook
- Author:
- Megan Sherbenou
- Date Added:
- 06/27/2024

Through two lessons and five activities, students explore the structure and function of cell membranes. Specific transport functions, including active and passive transport, are presented. In the legacy cycle tradition, students are motivated with a Grand Challenge question. As they study the ingress and egress of particles through membranes, students learn about quantum dots and biotechnology through the concept of intracellular engineering.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Physical Science
- Technology
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Melinda M. Higgins
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

Students are presented with a real-life problem as a challenge to investigate, research and solve. Specifically, they are asked to investigate why salt water helps a sore throat, and how engineers apply this understanding to solve other problems. Students read a medical journal article and listen to an audio talk by Dr. Z. L. Wang to learn more about quantum dots. After students reflect and respond to the challenge question, they conduct the associated activity to perform journaling and brainstorming.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Technology
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Melinda Higgins
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

Insert channels in a membrane and see what happens. See how different types of channels allow particles to move through the membrane.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Simulation
- Provider:
- University of Colorado Boulder
- Provider Set:
- PhET Interactive Simulations
- Author:
- John Blanco
- Katherine Perkins
- Noah Podolefsky
- Date Added:
- 03/08/2011
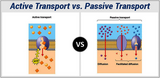
The real structure of cell membrane is so dynamic & it not only allows the cells to move but also has constant movement & fluidity. Therefore, an animation would be great for teaching the dynamic movement of phospholipids & proteins in cell membrane. This LO also helps students to understand the movement of material across the membrane. I prefer students watch it at least twice.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Author:
- maxwell sanei
- Date Added:
- 03/03/2018

This course develops and applies scaling laws and the methods of continuum and statistical mechanics to biomechanical phenomena over a range of length scales, from molecular to cellular to tissue or organ level.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Grodzinsky, Alan
- Kamm, Roger
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2015