74 Results


Students compare and contrast passive and active transport by playing a game to model this phenomenon. Movement through cell membranes is also modeled, as well as the structure and movement typical of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Concentration gradient, sizes, shapes and polarity of molecules determine the method of movement through cell membranes. This activity is associated with the Test your Mettle phase of the legacy cycle.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Applied Science
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Melinda M. Higgins
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014
Meiosis is important in assuring genetic diversity in sexual reproduction. Use this interactive animation to follow Meiosis I (reduction division) and Meiosis II in a continuous sequence or stop at any stage and review critical events.
- Subject:
- Education
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Interactive
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- SMARTR
- Provider Set:
- SMARTR: Virtual Learning Experiences for Youth
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2010

This animation demonstrates the stages of mitosis in an animal cell. Use the control buttons in the upper left to run the complete animation. Click on any intermediate stage (for example, Anaphase), and see a representative still frame.
- Subject:
- Education
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Interactive
- Provider:
- SMARTR
- Provider Set:
- SMARTR: Virtual Learning Experiences for Youth
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2010
Try your hand at assembling the following animal cell jigsaw puzzle created with an image from CELLS alive! This puzzle is 32 pieces and generally takes a few minutes to solve. Have fun!
- Subject:
- Education
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Diagram/Illustration
- Provider:
- SMARTR
- Provider Set:
- SMARTR: Virtual Learning Experiences for Youth
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2010
This site is a searchable encyclopedia of thousands of photos, descriptions, sound recordings, and other information about individual animal species. Find out about amphibians, arthropods, birds, fishes, insects, mammals, mollusks, reptiles, and sharks. Explore special features on mammals, skulls, and frog calls. Students are invited to contribute.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Zoology
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Provider:
- NSDL Staff
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2008
This is a great site to learn about apoptosis. It includes pictures, information, and links to other great sites on apoptosis. There is also a video that is available for download.
- Subject:
- Education
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- SMARTR
- Provider Set:
- SMARTR: Virtual Learning Experiences for Youth
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2010
This is a Introduction to microbiology course. The content of this module is syllabus as well as powerpoint slides presentation, using OpenStax Microbiology textbook. Content uploaded by Joanna Gray. All content created by Jaleh E. Jalili

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 08/22/2012
Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. This version has been adapted by faculty at Austin Community College. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Date Added:
- 02/13/2019

Life is all around us, both as multicellular organisms such as the iguana and bamboo above, as well as the unicellular microorganisms such as bacteria. Life is present on every continent, in the air and in the waters of the world. There is life even in the Mariana Trench, seven miles below the surface of the ocean. As of 2010 biologists have described and classified 1.7 million plants and animals, and estimate that there are till over five million species still undiscovered.This chapter will introduce the ways we study the science of Biology in the twenty-first century, the characteristics of living organisms and their classification.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
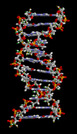
Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy that can be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules. A molecule is a chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by one or more chemical bonds. Many molecules that are biologically important are macromolecules, large molecules that are typically formed by polymerization (a polymer is a large molecule that is made by combining smaller units called monomers, which are simpler than macromolecules). An example of a macromolecule is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (Figure 1.15), which contains the instructions for the structure and functioning of all living organisms.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify and describe the properties of lifeDescribe the levels of organization among living thingsRecognize and interpret a phylogenetic treeList examples of different sub disciplines in biology
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify and describe the properties of lifeDescribe the levels of organization among living thingsRecognize and interpret a phylogenetic treeList examples of different sub disciplines in biology
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 08/17/2019

This course focuses on feedback control mechanisms that living organisms implement at the molecular level to execute their functions, with emphasis on techniques to design novel systems with prescribed behaviors. Students will learn how biological functions can be understood and designed using notions from feedback control.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Del Vecchio, Domitilla
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2015

This subject deals primarily with kinetic and equilibrium mathematical models of biomolecular interactions, as well as the application of these quantitative analyses to biological problems across a wide range of levels of organization, from individual molecular interactions to populations of cells.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Tidor, Bruce
- Wittrup, Karl
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2004