
Laboratory manual for undergraduate Anatomy & Physiology 2
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Biology
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Reading
- Teaching/Learning Strategy
- Textbook
- Author:
- Julie Robinson
- Date Added:
- 07/30/2022

Laboratory manual for undergraduate Anatomy & Physiology 2
Anatomy and Physiology is a dynamic textbook for the two-semester human anatomy and physiology course for life science and allied health majors. The book is organized by body system and covers standard scope and sequence requirements. Its lucid text, strategically constructed art, career features, and links to external learning tools address the critical teaching and learning challenges in the course. The web-based version of Anatomy and Physiology also features links to surgical videos, histology, and interactive diagrams.
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
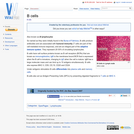
So named as they were initially found in the Bursa of Fabricius, B cells produce antibodies and are associated with humoral immunity (T cells are part of the cell-mediated immune response), and are an integral part of the adaptive immune system. They represent 20-30% of circulating lymphocytes.

Basophils are derived from the same stem cell line as mast cells and while they are similar to mast cells, they are not identical (they are thought by some to be immature mast cells). They are the least common of all the leukocytes, are a similar size to neutrophils and eosinophils and are characterised by the large number of basophilic staining granules in their cytoplasm. They are present in the circulation but rarely found in tissue.

Mature B cells that undergo stimulation by an antigen undergo class switching, and differentiate into either plasma or memory cells. In the paracortex region of the lymph node binding to MHC II in the presence of IL-4 produced by the CD4+ T cells (TH2 type) causes the B cells to differentiate; most will become plasma cells, however a small number will become memory cells. Follicular dendritic cells present in the germinal centers of peripheral lymphoid organs can absorb intact antigen onto their surface to present to B cells to stimulate differentiation.

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe epithelial tissuesDiscuss the different types of connective tissues in animalsDescribe three types of muscle tissuesDescribe nervous tissue

By the end of this section, you will be able to:List the basic components of the bloodCompare red and white blood cellsDescribe blood plasma and serum
By the end of this section, you will be able to:List the basic components of the bloodCompare red and white blood cellsDescribe blood plasma and serum


Students will make a proportional model of blood out of red gelatin, a plastic bag, and rice. They will learn about the different components that make up blood and will investigate what happens when the arteries and veins experience buildup from cholesterol. They will then work in pairs to brainstorm ways to clean our clogged arteries.
Students are introduced to the circulatory system with an emphasis on the blood clotting process, including coagulation and the formation and degradation of polymers through their underlying atomic properties. They learn about the medical emergency of strokes the loss of brain function commonly due to blood clots including various causes and the different effects depending on the brain location, as well as blood clot removal devices designed by biomedical engineers.
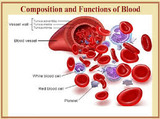
Blood : Structure and Function

Blood : Structure and Function
This unit describes the blood, lymphatic and immune systems.
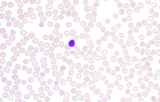
This video shows scanning a Wright's stained blood smear slide with pauses to view leukocytes. The video was taken at 630X under a brightfield microscope. This video is compatible with a laboratory lesson in which students observe, categorize, and count leukocytes. More than 100 leukocytes are viewed in this video. Note, this video does not have narration.Video credit: Emily Fox