5975 Results


Life is all around us, both as multicellular organisms such as the iguana and bamboo above, as well as the unicellular microorganisms such as bacteria. Life is present on every continent, in the air and in the waters of the world. There is life even in the Mariana Trench, seven miles below the surface of the ocean. As of 2010 biologists have described and classified 1.7 million plants and animals, and estimate that there are till over five million species still undiscovered.This chapter will introduce the ways we study the science of Biology in the twenty-first century, the characteristics of living organisms and their classification.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy that can be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules. A molecule is a chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by one or more chemical bonds. Many molecules that are biologically important are macromolecules, large molecules that are typically formed by polymerization (a polymer is a large molecule that is made by combining smaller units called monomers, which are simpler than macromolecules). An example of a macromolecule is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (Figure 1.15), which contains the instructions for the structure and functioning of all living organisms.
What is biology? In simple terms, biology is the study of living organisms and their interactions with one another and their environments. This is a very broad definition because the scope of biology is vast. Biologists may study anything from the microscopic or submicroscopic view of a cell to ecosystems and the whole living planet (Figure 1.2). Listening to the daily news, you will quickly realize how many aspects of biology are discussed every day. For example, recent news topics include Escherichia coli (Figure 1.3) outbreaks in spinach and Salmonella contamination in peanut butter. Other subjects include efforts toward finding a cure for AIDS, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. On a global scale, many researchers are committed to finding ways to protect the planet, solve environmental issues, and reduce the effects of climate change. All of these diverse endeavors are related to different facets of the discipline of biology.

Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) (Figure 1.5), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost all fields of study as a logical, rational problem-solving method.

Biology is the science that studies life, but what exactly is life? This may sound like a silly question with an obvious response, but it is not always easy to define life. For example, a branch of biology called virology studies viruses, which exhibit some of the characteristics of living entities but lack others. It turns out that although viruses can attack living organisms, cause diseases, and even reproduce, they do not meet the criteria that biologists use to define life. Consequently, virologists are not biologists, strictly speaking. Similarly, some biologists study the early molecular evolution that gave rise to life; since the events that preceded life are not biological events, these scientists are also excluded from biology in the strict sense of the term.
This 11-minute video lesson provides a review of B cells, CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells. [Biology playlist: Lesson 57 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 16-minute video lesson looks at the role of phagocytes in innate or nonspecific immunity. It also discusses neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells. MHC II. [Biology playlist: Lesson 51 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 15-minute video lesson looks at the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in controlling calcium ion concentrations within the muscle cell. [Biology playlist: Lesson 49 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 14-minute video lesson looks at secondary active transport in the Nephron. [Biology playlist: Lesson 60 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 14-minute video lesson covers the chromosomal basis for gender and sex-linked traits. [Biology playlist: Lesson 17 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 14-minute video lesson looks at how a sodium potassium pump can maintain a voltage gradient across a cell or neuron's membrane. [Biology playlist: Lesson 42 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Salman Khan
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
This 13-minute video lesson looks at the science of taxonomy and where humans fit into the tree of life. [Biology playlist: Lesson 62 of 71].
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Khan
- Salman
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2012
CK-12 Biology Teacher's Edition complements the CK-12 Biology Student Edition FlexBook.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Textbook
- Provider:
- CK-12 Foundation
- Provider Set:
- CK-12 FlexBook
- Author:
- Brainard, Jean
- Wilkin, Douglas (Editor)
- Date Added:
- 07/20/2011

The MIT Biology Department supports TAs’ teaching by providing a specialized Teaching Assistant (TA) training program in Biology Pedagogy, for which TAs can earn a training certificate. This program has been developed in response to the feedback of previous TAs, and is designed to actively meet each TA’s needs as they are teaching. It provides practical knowledge that directly relates to their teaching responsibilities each week, and provides them with the opportunity to practice different skills and techniques in a supportive environment.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Education
- Higher Education
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Morrill, Summer
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2021
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
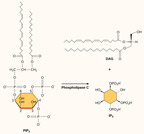
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain how the binding of a ligand initiates signal transduction throughout a cellRecognize the role of phosphorylation in the transmission of intracellular signalsEvaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017