Short video on the somatosensory system for anatomy and physiology.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Applied Science
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Author:
- Dr. Bruce Forciea
- Date Added:
- 04/05/2018

Short video on the somatosensory system for anatomy and physiology.

n the verterbrate embryo, as the primitive streak is regressing, the paraxial mesoderm divides into blocks of cells called somites. These divisions can be seen either side of the notochord. Somites are transient structures that will give rise to cells of the vertebrae and ribs, dermis of the dorsum, skeletal muscle of the body wall, back and limbs. Somites begin to develop at the anterior of the embryo first, and appear at regular intervals.
Why do humans have two ears? How do the properties of sound help with directional hearing? Students learn about directional hearing and how our brains determine the direction of sounds by the difference in time between arrival of sound waves at our right and left ears. Student pairs use experimental set-ups that include the headset portions of stethoscopes to investigate directional hearing by testing each other's ability to identify the direction from which sounds originate.
In our new Species at Risk (SAR) education kit, each lesson addresses a species at risk through an Ocean Wise conservation initiative. Students will learn about the humpback whale and climate change, the killer whale and ocean pollution, the great white shark and bycatch, the hawksbills sea turtle and plastic pollution, and the sea otter and loss of kelp habitat, plus ways to take action to protect them! Equipped with the proper knowledge and tools, students will acquire an impactful learning experience to empower them to become ocean champions and stewards for species at risk.
The Earth’s ocean and its interconnected systems depend on marine species to maintain the efficiency and balance of the functioning of their ecosystems. Their role in the ocean has a direct impact on its health and our own. And yet, every day, thousands of animals fall victim to anthropogenic threats imposed on the ocean by human activity. It is going to take a deep, transformational change in humanity’s consciousness and behaviours regarding our oceans to ensure the protection of species. We believe this is possible by providing climate and conservation education to our youth to raise awareness on the interconnectedness between our lives and the ocean, and the importance of the role that each species holds on our planet.

Fusion of the two plates of the thyroid cartilage is incomplete forming a rostral pointing notch which is a good site for surgical entry into the larynx. The thyroarytenoid muscle is divided into 2 parts; the rostral and caudal vocalis, which are situated within the vocal folds and vestibular folds. The cuneiform processes are attached to the epiglottis.
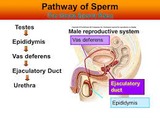
Pathway of sperm from testes to penis in under one minute.

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Understanding how human decision-making and preferences manifest before conscious thought has long challenged researchers focused on cognitive and information science. Now, the field of neuromarketing – a discipline that looks at the neurocognitive underpinnings of consumer behavior – is starting to uncover, in amazing detail, exactly how the brain goes about recognizing a brand. An international research team based in Auckland University of Technology and Nottingham Trent University has devised a new machine learning method that tracks brain responses to logos on the millisecond timescale…even before conscious thoughts are formed. Their results shed light on the early spikes in brain activity that are tied to brand awareness. The method utilizes one of the most promising recent trends in artificial intelligence research: spiking neural networks. These networks use algorithms loosely modeled on the behavior of the human brain to recognize patterns in sets of streaming data..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.

The spinal cord is constructed of the marginal layer which has axons and white matter, the mantle which contains cell bodies and grey matter and the spinal canal. This canal conducts sensory information from the peripheral nervous system (both somatic and autonomic) to the brain, conducts motor information from the brain to various effectors and acts as a minor reflex center.
Short video on spinal cord anatomy for anatomy and physiology.

In this lesson the students will learn how the heart functions. Students will be introduced to the concept of action potential generation. The lesson will explain how action potential generation causes the electrical current that causes muscle contraction in the heart. Students will be introduced to the basic electrical signal generated by the heart; P, QRS, and T waves. The lesson will approach the heart from an engineering standpoint and encourage students to design ways to improve heart function. Students will also learn the basic steps of the engineering design process.

In this video we explore the organization of the nervous system, and its division into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Created by Matthew Barry Jensen.

The last epic tale of a lost soul
Word Count: 23878
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

This page explains superficial anatomy through a guide to the superficial anatomy of a dog, including the head, forelimb, and hindlimb. Detailed Illustrations open in new tab.
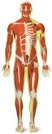
Superficial muscles of the human body.
Hank tries not to stress you out too much as he delves into the functions and terminology of your sympathetic nervous system.
Chapters:
Introduction: Physiology of Stress
How Signals Travel to Effectors
Hormones & Neurotransmitters Communicate Stress
Preganglionic Fibers Release Acetylcholine (ACh)
Postganglionic Fibers Release Norepinephrine
Adrenal Glands Release Norepinephrine and Epinephrine as Hormones
Neurotransmitters vs. Hormones
How Norepinephrine Works: Alpha and Beta Receptors
Review
Credits
Short video covering common sympathetic nervous system drugs.

Neurons communicate with each other and relay information to the brain through synapse. Influx of calcium through ion channels acts as a trigger for starting the neurotransmission cascade, which upon reaching action potential, leads to the release of neurotransmitters, propagating the signal from the pre-synaptic membrane to the post-synaptic membrane.

"Future Ready" is a comprehensive open education resource that highlights practical steps for maintaining physical health, overall wellness, and embracing individuality. It addresses the impact of technology, the role of parents and doctors in protecting teenagers, and the importance of virtues for decision-making and fulfillment. The guide encourages teenagers to challenge themselves physically, manage emotions effectively, and use proactive language for self-control.
Ce document est un fascicule de TP de l'étude de la régulation de la glycémie chez le rat.
Hank resists the urge to devour a slice of pizza so that he can walk you through the way we experience our major special senses. It all boils down to one thing: sensory cells translate chemical, electromagnetic, and mechanical stimuli into action potentials that our nervous system can make sense of. Today we're focusing on smell (olfaction) and taste (gustation), which are chemical senses that call on chemoreceptors. As usual, we'll begin with a quick look at how these things can go wrong.
Chapters:
Introduction: Anosmia
How Smell Works
Olfactory Epithelium
Olfactory Sensory Neurons
Glomerulus
How the Brain Processes Smell
How Taste Works
What Are Taste Buds (Taste Receptor Epithelial Cells)?
Types of Taste Receptor Epithelial Cells: Gustatory and Basal
How Different Tastants are Sensed
Review
Credits