Fundamental frequencies (first harmonics) of strings.
- Subject:
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 04/11/2016

Fundamental frequencies (first harmonics) of strings.

The electric field lines from a point charge evolve in time as the charge moves. Watch radiation propagate outward at the speed of light as you wiggle the charge. Stop a moving charge to see bremsstrahlung (braking) radiation. Explore the radiation patterns as the charge moves with sinusoidal, circular, or linear motion. You can move the charge any way you like, as long as you don���������t exceed the speed of light.

Using a systems framework, this textbook provides a clear and comprehensive introduction to the performance, analysis, and design of radio systems for students and practicing engineers. Presented within a consistent framework, the first part of the book describes the fundamentals of the subject: propagation, noise, antennas, and modulation. The analysis and design of radios including RF circuit design and signal processing is covered in the second half of the book.
Key features
- Numerous examples within the text involve realistic analysis and design activities, and emphasize how practical experiences may differ from theory or taught procedures.
- RF circuit design and analysis is presented with minimal involvement of Smith charts, enabling students to more readily grasp the fundamentals.
- Both traditional and software-defined/direct sampling technology are described with pros and cons of each strategy explained.
- 517 pages. Licensed CC BY NC 4.0.
"This textbook gives engineering students a complete overview of radio systems and provides practicing wireless engineers with a convenient comprehensive reference."
- Patrick Roblin, Ohio State University
Radio Systems Engineering, Revised First Edition was previously published by Cambridge University Press (2016) ISBN 9781107068285. This version is © Steven W. Ellingson and has been lightly updated to correct known errata, minor issues with text and figures, and to present examples in color highlight boxes and some figures in color. It is made freely available and under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial International License (CC BY NC 4.0).
Are you reviewing or adopting this book for a course?
Please help us understand your use by filling out this form: https://bit.ly/interest_radiosystemsengineering_revised1st
Join the instructor group (https://oercommons.org/groups/radio-systems-engineering-instructor-group/14443/) to connect with other instructors interested in this resource.
How to access the book
The main landing page for this book is https://doi.org/10.21061/radiosystemsengineering-revised1st.
The open textbook is freely available online in multiple formats including PDF and HTML [forthcoming].
A paperback print version (in color) is available for order here: https://www.amazon.com/Radio-Systems-Engineering-Revised-First/dp/1957213752
ISBNs
ISBN (PDF): 978-1-957213-76-7
ISBN (HTML): 978-1-957213-77-4 (accessible version forthcoming)
ISBN (print): 978-1-957213-75-0
Table of contents
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Antenna Fundamentals
Chapter 3: Propagation
Chapter 4: Noise
Chapter 5: Analog Modulation
Chapter 6: Digital Modulation
Chapter 7: Radio Link Analysis
Chapter 8: Two-Port Concepts
Chapter 9: Impedance Matching
Chapter 10: Amplifiers
Chapter 11: Linearity, Multistage Analysis, and Dynamic Range
Chapter 12: Antenna Integration
Chapter 13: Analog Filters & Multiplexers
Chapter 14: Frequency and Quadrature Conversion in the Analog Domain
Chapter 15: Receivers
Chapter 16: Frequency Synthesis
Chapter 17: Transmitters
Chapter 18: Digital Implementation of Radio Functions
Appendix A: Empirical Modeling of Mean Path Loss
Appendix B: Characteristics of Some Common Radio Systems
About the author
Dr. Steven W. Ellingson
Steven W. Ellingson is an Associate Professor of Electrical & Computer Engineering at Virginia Tech. He received the Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Ohio State University. He held senior engineering positions at Booz-Allen & Hamilton, Raytheon, and the Ohio State University ElectroScience Laboratory before joining the faculty of Virginia Tech. His research is in the areas of antennas and propagation, applied signal processing, and radio frequency instrumentation, with funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, and the commercial communications and aerospace industries. Dr. Ellingson serves as a consultant to industry and government on topics pertaining to radio frequency systems.
Suggested citation
Ellingson, Steven W. (2023). Radio Systems Engineering, Revised First Edition. Blacksburg. https://doi.org/10.21061/radiosystemsengineering-revised1st. Licensed with CC BY NC 4.0.
View Errata: https://bit.ly/errata_radiosystemsengineering_revised1st
Report an Error: https://bit.ly/reporterror_radiosystemsengineering_revised1st
Accessibility
Virginia Tech is committed to making its publications accessible in accordance with the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990.

Broadcast radio waves from KPhET. Wiggle the transmitter electron manually or have it oscillate automatically. Display the field as a curve or vectors. The strip chart shows the electron positions at the transmitter and at the receiver.

Broadcast radio waves from KPhET. Wiggle the transmitter electron manually or have it oscillate automatically. Display the field as a curve or vectors. The strip chart shows the electron positions at the transmitter and at the receiver.
Through this lesson students learn how AM radios work through basic concepts about waves and magnetic fields. Waves are first introduced by establishing the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves, as well as identifying the amplitude and frequency of a given waveform. Students then learn general concepts about magnetic fields, leading into how radio waves are created and transmitted. Several demonstrations can be performed in order to help students better understand these concepts. The goal of this lesson is for students to understand how the AM radios built during the associated activity function.

Students examine the existence of sound by listening to and seeing sound waves while conducting a set of simple activities as a class or in pairs at stations. Students describe sound in terms of its pitch, volume and frequency. They use this knowledge to discuss how engineers study sound waves to help people who cannot hear or talk.
Students learn about the types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes and how they move the Earth. The dangers of earthquakes are presented as well as the necessity for engineers to design structures for earthquake-prone areas that are able to withstand the forces of seismic waves. Students learn how engineers build shake tables that simulate the ground motions of the Earth caused by seismic waves in order to test the seismic performance of buildings.
Students work with partners to create four different instruments to investigate the frequency of the sounds they make. Teams may choose to make a shoebox guitar, water-glass xylophone, straw panpipe or a soda bottle organ (or all four!). Conduct this activity in conjunction with Lesson 3 of the Sound and Light unit.
This interactive simulation, adapted from the University of Colorado's Physics Education Technology project, illustrates sound waves. Adjust the frequency and amplitude to see and hear how the waves change.

This simulation lets you see sound waves. Adjust the frequency or volume and you can see and hear how the wave changes. Move the listener around and hear what she hears.

This simulation lets you see sound waves. Adjust the frequency or volume and you can see and hear how the wave changes. Move the listener around and hear what she hears.
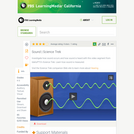
How to find the amplitude, period, frequency, and wavelength for a sound wave. Created by David SantoPietro.

Students learn about sound and sound energy as they gather evidence that sound travels in waves. Teams work through five activity stations that provide different perspectives on how sound can be seen and felt. At one station, students observe oobleck (a shear-thickening fluid made of cornstarch and water) “dance” on a speaker as it interacts with sound waves (see Figure 1). At another station, the water or grain inside a petri dish placed on a speaker moves and make patterns, giving students a visual understanding of the wave properties of sound. At another station, students use objects of various materials and shapes (such as Styrofoam, paper, cardboard, foil) to amplify or distort the sound output of a homemade speaker (made from another TeachEngineering activity). At another station, students complete practice problems, drawing waves of varying amplitude and frequency. And at another station, they experiment with string (and guitar wire and stringed instruments, if available) to investigate how string tightness influences the plucked sound generated, and relate this sound to high/low frequency. A worksheet guides them through the five stations. Some or all of the stations may be included, depending on class size, resources and available instructors/aides, and this activity is ideal for an engineering family event.

Students are provided with an understanding of sound and light waves through a "sunken treasure" theme a continuous storyline throughout the lessons. In the first five lessons, students learn about sound, and in the rest of the lessons, they explore light concepts. To begin, students are introduced to the concepts of longitudinal and transverse waves. Then they learn about wavelength and amplitude in transverse waves. In the third lesson, students learn about sound through the introduction of frequency and how it applies to musical sounds. Next, they learn all about echolocation what it is and how engineers use it to "see" things in the dark or deep underwater. The last of the five sound lessons introduces acoustics; students learn how different materials reflect and absorb sound.
Echolocation is the ability to orient by transmitting sound and receiving echoes from objects in the environment. As a result of a Marco-Polo type activity and subsequent lesson, students learn basic concepts of echolocation. They use these concepts to understand how dolphins use echolocation to locate prey, escape predators, navigate their environment, such as avoiding gillnets set by commercial fishing vessels. Students will also learn that dolphin sounds are vibrations created by vocal organs, and that sound is a type of wave or signal that carries energy and information especially in the dolphin's case. Students will learn that a dolphin's sense of hearing is highly enhanced and better than that of human hearing. Students will also be introduced to the concept of by-catch Students will learn what happens to animals caught through by-catch and why.
Music can loosely be defined as organized sound. The lesson objectives, understanding sound is a form of energy, understanding pitch, understanding sound traveling through a medium, and being able to separate music from sound, can provide a good knowledge base as to how sound, math, and music are related. Sound exists everywhere in the world; typically objects cause waves of pressure in the air which are perceived by people as sound. Among the sounds that exist in everyday life, a few of them produce a definite pitch. For example, blowing air over half full glass bottles, tapping a glass with a spoon, and tapping long steel rods against a hard surface all produce a definite pitch because a certain component of the object vibrates in a periodic fashion. The pitch produced by an object can be changed by the length or the volume of the portion that vibrates. For example, by gradually filling a bottle while blowing across the top, higher pitches can be generated. By organizing a few of these sounds with a clearer pitch, the sounds become closer to music. The very first musical instruments involved using various objects (e.g. bells) that have different pitches, which are played in sequence. The organization of the pitches is what transforms sounds into music. Since the first instruments, the ability to control pitch has greatly improved as illustrated by more modern instruments such as guitars, violins, pianos, and more. Music is comprised of organized sound, which is made of specific frequencies. This lesson will help define and elaborate on the connections between sound and music.
How fast does sound actually travel? Created by David SantoPietro.
Find out why you can make music by blowing into empty bottles. Created by David SantoPietro.
Find out why a flute makes such specific notes. Created by David SantoPietro.