Microorganisms in action!
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Assessment
- Game
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- Arizona State University
- Provider Set:
- Ask A Biologist
- Author:
- Dr. Biology
- Date Added:
- 06/10/2009

Microorganisms in action!

Course materials including an instructor guide, course map, and weekly schedule for the third part of a three-part Anatomy and Physiology class. Includes learning objectives, assignments, formative feedback, learning activities, and readings from the OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology 2e open textbook.

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"The Wnt signaling pathway is linked to multiple developmental defects, inherited diseases, and many types of cancer. An essential component of the Wnt signaling pathway is a family of proteins known as Dishevelled (DVL). Studies have hinted that phosphorylation of DVL proteins at specific sites ultimately controls parts of the Wnt pathway, but the molecular mechanisms have remained unclear. Now, researchers have discovered “barcode”-like patterns of phosphorylation that could dictate certain DVL functions. The team used mass spectrometry-based proteomics to determine which sites along the protein DVL3 were phosphorylated by 8 different kinases and found 88 phosphorylation sites organized into barcodes unique for each kinase. The barcoding they observed could determine how DVL3 is distributed in the cell and, with further research, could point to the role of DVL proteins in certain human diseases and cancers..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.

In this interactive demonstration students will make observations of diffusion of a semi permeable membrane and be able to compare these observations to the functions of a cell membrane.
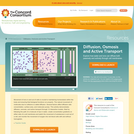
Movement of ions in and out of cells is crucial to maintaining homeostasis within the body and ensuring that biological functions run properly. The natural movement of molecules due to collisions is called diffusion. Several factors affect diffusion rate: concentration, surface area, and molecular pumps. This activity demonstrates diffusion, osmosis, and active transport through 12 interactive models.

Introduction to the egg, sperm, and fertilization. Created in collaboration between the Association of American Medical Colleges and Khan Academy.

An overview of the membrane-bound structures that form the endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells.

Structure of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body (Golgi apparatus). Their role in protein secretion. Created by Sal Khan.

Introduction to extranuclear inheritance (part 1).

How haploid gametes (sperm and egg cells) combine to form a diploid zygote with two sets of chromosomes. Created by Sal Khan.

The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a tapestry of several types of molecules (phospholipids, cholesterols, and proteins) that are constantly moving. This movement helps the cell membrane maintain its role as a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell environments.

This textbook is focused specifically on the principles and concepts of a foundational Cell Biology course. The book takes a more conceptual approach that highlights how scientists study cells, and how to analyze and interpret experimental results. Rather than focusing primarily on historical experiments that were key to our understanding of cells, the book explores a range of more modern experimental techniques so that students can begin to understand how cells are studied now, in the 21st century. The book includes over 200 newly created illustrations and animations, that were specifically designed for this book, as well as review questions at the end of each chapter, to help students explore and understand the material.

Learn about how g protein coupled receptors work in the cell membrane. Created by William Tsai.

Students are given a problem about a relatively new treatment for cancer, Gleevec, and asked to apply and synthesize what they have learned about cell signaling and the eukaryotic cell cycle to explain why this targeted treatment works to prevent cell division with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapeutic agents.
Join Stuart Lipton of The Burnham Institute and discover important anti-aging strategies, the latest drugs for degenerative disorders such as AlzheimerŐs disease and the potential use of human stem cells for neurological conditions. (57 minutes)
This book is a guide to the basic histology lab conducted as a part of the Queens College, CUNY Biology Department Bio105 General Biology: Physiology and Cell Biology course. This course is the first half our two-part series for biology majors. The actives are designed to be conducted over a single 3-hour lab periods which focus on the relationship of form and function of the cellular and organ level anatomy and physiology. Step by step instructions for each slide set are provided for all the key organs.
In addition to the full text of the book, we also provide a checklist form with just the assessment portions of the book. This is to help summarize all the information the student should get from the activity.

This activity is a lab investigation is which students will design and conduct an experiment related to movement of materials through a cell membrane. Modified from a lab I received from a fellow teacher, Jeanne M. Reed.
The first video in our Cell Biology Lecture, part of our Anatomy and Physiology lecture series.
This video introduces us to both cell biology and cell theory. To see the rest of our series please be sure to check out http://www.mrfordsclass.net
Our second video from the cell biology lesson, part of our anatomy and physiology lecture series.
This video gives a brief summary of the differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
All of our videos can be found at http://www.mrfordsclass.net
The concepts covered in this video include:
•Eukaryotes
•Prokaryotes