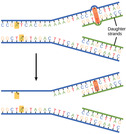
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss the different types of mutations in DNAExplain DNA repair mechanisms
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss the different types of mutations in DNAExplain DNA repair mechanisms

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss the similarities and differences between DNA replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotesState the role of telomerase in DNA replication
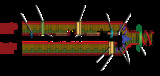
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotesDiscuss the role of different enzymes and proteins in supporting this process
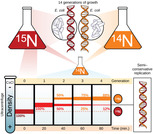
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain how the structure of DNA reveals the replication processDescribe the Meselson and Stahl experiments

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the structure of DNAExplain the Sanger method of DNA sequencingDiscuss the similarities and differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain transformation of DNADescribe the key experiments that helped identify that DNA is the genetic materialState and explain Chargaff’s rules


An introduction to cellular and molecular biology. Major topics include the biochemical basis of life, cell biology, photosynthesis, respiration, mitosis, meiosis, genetics, DNA structure and replication and protein synthesis. Students engage the scientific method by designing, conducting and evaluating laboratory experiences that include selected topics in cell structure and function, enzymes, respiration, photosynthesis, genetics and molecular biology. NOTE: Students may receive credit for BIO 119 or BIO 126, but not for both.

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
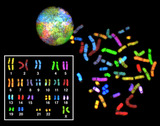
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomesDistinguish between chromosomes, genes, and traitsDescribe the mechanisms of chromosome compaction


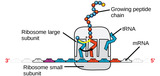
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the structure of nucleic acids and define the two types of nucleic acidsExplain the structure and role of DNAExplain the structure and roles of RNA
CK-12 Biology Workbook complements its CK-12 Biology book.

This site contains user-friendly tools to launch DNA database searches, statistical analyses, and population modeling from a centralized workspace. Educational databases support investigations of an Alu insertion polymorphism on human chromosome 16 and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the human mitochondrial control region.