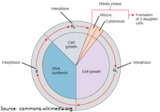
Students will create a 360-degree, interactive tour of the cell cycle.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Material Type:
- Assessment
- Author:
- Michelle Adams
- Date Added:
- 03/04/2020

Students will create a 360-degree, interactive tour of the cell cycle.

Internet scavenger hunt activity with worksheet

Mechanical forces play a decisive role during development of tissues and organs, during remodeling following injury as well as in normal function. A stress field influences cell function primarily through deformation of the extracellular matrix to which cells are attached. Deformed cells express different biosynthetic activity relative to undeformed cells. The unit cell process paradigm combined with topics in connective tissue mechanics form the basis for discussions of several topics from cell biology, physiology, and medicine.

Students color-code a schematic of a cell and its cell membrane structures. Then they complete the "Build-a-Membrane" activity found at http://learn.genetics.utah.edu. This reinforces their understanding of the structure and function of animal cells, and shows them the importance of being able to construct a tangible model of something that is otherwise difficult to see.

Worksheet that goes over the types of transport associated with a cell membrane.

Students learn about the different structures that comprise cell membranes, fulfilling part of the Research and Revise stages of the legacy cycle. They view online animations of cell membrane dynamics (links provided). Then they observe three teacher demonstrations that illustrate diffusion and osmosis concepts, as well as the effect of movement through a semi-permeable membrane using Lugol's solution.

This is a video and supporting worksheet covering membrane transport processes (Chapter 3).
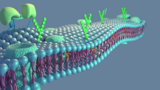
Welcome to 'Cell Membranes - Composition and Passive Transport' ModuleBy the end of this module, students will be able to: - Understand the structure, composition, and function of the cell membrane - Recognize how the membrane effects the rest of the cell and the larger organism- Visualize key concepts through our instructional video- Recall knowledge with our self-quiz of key concepts presented in both the module and the video- Critically apply this information through our in-class activityScroll down for more information on resources available in this module.GIF by Amoeba SistersResources:Cell Membrane Handout (thorough explanation of material, 5 pages long)Cell Membrane Instructional Video (Stuti and Scarlett visually present the process of passive transport)Khan Academy Diffusion and Passive Transport Article With Images (This article provides a shorter summary of Diffusion and Passive Transport with images for visual comprehension.)Cell Membrane Key Concepts & Comprehension Questions (List of key concepts presented in the Handout and Video, followed by comprehension questions)Cell Membrane Self-Quiz (Test your memorization of key concepts)Cell Membrane In-class Activity (Apply your knowledge of key concepts to the greater picture)Answer Key for In-class Activity (Compare your answers, and work on problems areas with Cell Membrane Handout, Key Concepts, or Video.)Cell Membrane Case Study (Evaluate your knowledge by applying it to this case study about how passive transport relates to digestion and diarrhea.)Website, resources, and content created by Stuti Patel, Ifrah Raja, Rubiya Dhillon, Kate Wilcox, and Scarlett Leon.
The cell membrane is a protein-studded phospholipid bilayer that not only protects our cells, but also regulates what goes in and out. In this episode of Crash Course Biology, we’ll look at the structure of the bilayer, learn about its discovery, and explore the many ways substances can be transported into and out of cells.
Chapters:
Introduction to the Cell Membrane
Membrane Structure
Membrane Proteins
Membrane Transport
Review & Credits
Credits
This is a video and worksheet covering the basics of cell membranes (Anatomy and Physiology 2e, Chapter 3).

This interactive lesson can be used by students to learn or review and practice animal and plant cell structures and function.

This is a hands on lab to model the energy in cells.
This lesson will require students to research the three tenets of cell theory and describe the scientific evidence that supports this theory. After students complete their research, they will engage in all steps of the writing process, including prewriting, outlining, revising, and editing. At the conclusion of the lesson, students will create a three-paragraph argumentative essay to examine the cell theory and the scientific evidence that supports this theory. This lesson results from a collaboration between the Alabama State Department of Education and ASTA.


A grasp of the logic and practice of science is essential to understand the rest of the world around us. To that end, the CMB3e iText (like earlier editions) remains focused on experimental support for what we know about cell and molecular biology, and on showing students the relationship of cell structure and function. Rather than trying to be a comprehensive reference book, CMB3e selectively details investigative questions, methods and experiments that lead to our understanding of cell biology. This focus is nowhere more obvious than in the chapter learning objectives and in external links to supplementary material. In the freely available Basic CMB3e, the latter include the author’s short just-in-time YouTube VOPs, embedded near relevant text.

Like most introductory science textbooks, this one opens with a discussion of scientific method. A key feature is its focus on experimental support for what we know about cell and molecular biology. Understanding how science is practiced and how investigators think about experimental results is essential to understanding the relationship of cell structure and function…, not to mention our relationship to the natural world. This is a free Open Education Resource (OER), covered by a Creative Commons CCBY license (check out the Preface!). Every chapter begins with learning objectives and links to relevant recorded lectures. As used by the author, the iText engages students with embedded “just-in-time” learning tools. These include instructor’s annotations (comments) directing students to animations or text of interest, as well as links to writing assignments and quizzes. These interactive features aim to strengthen critical thinking and writing skills necessary to understand cell and molecular biology, not to mention science as a way of thinking in general. Please excuse the marketing terms, but you can choose between Bronze, Silver, or Gold versions, reflecting increasing potential for student interaction with the iText. Download your choice of the iText or the sample chapter at one of the links below.

This course explores the major areas of cellular and molecular neurobiology, including excitable cells and membranes, ion channels and receptors, synaptic transmission, cell-type determination, axon guidance, neuronal cell biology, neurotrophin signaling and cell survival, synapse formation and neural plasticity. Material includes lectures and exams, and involves presentation and discussion of primary literature. It focuses on major concepts and recent advances in experimental neuroscience.

Overview of various cell cycle controls.

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, plays critical roles in animal development and in repair of DNA damage. Since DNA damage is a major factor in cancer development, identifying the regulators of damage-induced apoptosis could help researchers develop treatments. A recent study investigated whether NHR-14, an important developmental protein in the model organism C. elegans, also contributes to damage-induced apoptosis . using mutant C. elegans that are especially susceptible to radiation-induced DNA damage. Deletion of the gene encoding NHR-14, which corresponds to HNF4 in humans, decreased radiation-induced apoptosis of sex cells without affecting the levels of normal (non-damage-induced) apoptosis, indicating a specific role in the damage-induced death pathway. Further exploration revealed that the NHR-14 gene acts “downstream” of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway and regulates the transcription of the genes egl-1 and ced-13 after DNA is damaged..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.

Learn about how phospholipids form the cell membrane, and what types of molecules can passively diffuse thorugh the membrane. By William Tsai. . Created by William Tsai.