Topic : Rectilinear Motion
- Subject:
- Engineering
- Material Type:
- Lecture Notes
- Author:
- jones praveen j
- Date Added:
- 05/01/2020

Topic : Rectilinear Motion

UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW Basic concepts - concept of continuum, comparison of microscopic and macroscopic approach. Path and point functions. Intensive and extensive, total and specific quantities. System and their types. Thermodynamic Equilibrium State, path and process. Quasi-static, reversible and irreversible processes. Heat and work transfer, definition and comparison, sign convention. Displacement work and other modes of work .P-V diagram. Zeroth law of thermodynamics – concept of temperature and thermal equilibrium– relationship between temperature scales –new temperature scales. First law of thermodynamics –application to closed and open systems – steady and unsteady flow processes.UNIT II SECOND LAW AND AVAILABILITY ANALYSIS Heat Reservoir, source and sink. Heat Engine, Refrigerator, Heat pump. Statements of second law and its corollaries. Carnot cycle Reversed Carnot cycle, Performance. Clausius inequality. Concept of entropy, T-s diagram, Tds Equations, entropy change for - pure substance, ideal gases – different processes, principle of increase in entropy. Applications of II Law. High and low grade energy. Available and non-available energy of a source and finite body. Energy and irreversibility. Expressions for the energy of a closed system and open systems. Energy balance and entropy generation. Irreversibility. I and II law Efficiency.UNIT III PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCE AND STEAM POWER CYCLE Formation of steam and its thermodynamic properties, p-v, p-T, T-v, T-s, h-s diagrams. p-v-T surface. Use of Steam Table and Mollier Chart. Determination of dryness fraction. Application of I and II law for pure substances. Ideal and actual Rankine cycles, Cycle Improvement Methods - Reheat and Regenerative cycles, Economiser, preheater, Binary and Combined cycles.UNIT IV IDEAL AND REAL GASES, THERMODYNAMIC RELATIONS Properties of Ideal gas- Ideal and real gas comparison- Equations of state for ideal and real gases- Reduced properties-.Compressibility factor-.Principle of Corresponding states. –Generalised Compressibility Chart and its use-. Maxwell relations, Tds Equations, Difference and ratio of heat capacities, Energy equation, Joule-Thomson Coefficient, Clausius Clapeyron equation, Phase Change Processes. Simple Calculations.UNIT V GAS MIXTURES AND PSYCHROMETRY Mole and Mass fraction, Dalton’s and Amagat’s Law. Properties of gas mixture – Molar mass, gas constant, density, change in internal energy, enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs function. Psychrometric properties, Psychrometric charts. Property calculations of air vapour mixtures by using chart and expressions. Psychrometric process – adiabatic saturation, sensible heating and cooling,humidification, dehumidification, evaporative cooling and adiabatic mixing. Simple Applications
Instructional materials for the course "ENGR 1110: Engineering Graphics" include videos, assignments, slides, and drawings on the following topics: engineering graphics and scales, orthographic views, isometric views, dimensioning, section views, AutoCAD, layers, colors, mirrors, fillet, arrays, chamfer, blocks, Fusion 360, sheet metal modeling, tracing, textures, lofting and more.
Instructional materials for the course "ENTC 2160: Architectural CAD" include videos demonstrating how to create CAD drawings and use CAD tools. Videos cover the following topics: exterior walls, interior walls, doors, windows, dimensioning, linetypes, electrical, slab, stairs, hatching, fireplaces, and roofing.
Instructional materials for the course "ENTC 2170: Computer Aided Design and Drafting" include videos, assignments, slides, and drawings on the following topics: engineering graphics and scales, orthographic views, isometric views, dimensioning, section views, AutoCAD, layers, colors, mirrors, fillet, arrays, chamfer, blocks, Fusion 360, sheet metal modeling, tracing, textures, lofting and more.
This is a simple introduction on the basics of evaporation
Watch the fifth episode of our #EZScience series to learn how NASA uses balloon science to better understand our planet and universe.
This November, we celebrate 20 years of continuous human presence on the International Space Station--an incredible example of international cooperation.
In the latest episode of #EZScience, learn about the upcoming launch of Perseverance. Dr. E and Dr. Z talk about the technological advancements of the newest Mars rover (and helicopter!).
In the latest episode of #EZScience, learn about the science behind NASA's Perseverance rover that is targeted to launch to the Red Planet on July 30.
Watch the sixth episode of our #EZScience series to learn about the 30th anniversary of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is scheduled to touch down on the asteroid Bennu on October 20, 2020, for its first sample collection attempt.
Dr. E and Dr. Z will share exciting new discoveries being made by NASA and others, and explore their relationship to the Museum's one-of-a-kind collection.
In this "On the Go" episode of #EZScience, we're on the scene at Kennedy Space Center with the rocket that will take the Perseverance rover and the Ingenuity helicopter to Mars.
Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen and Dr. Ellen Stofan discuss the James Webb Space Telescope upcoming launch, as well as the Hubble Space Telescope backup mirror and historical spectrographs.
The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the basic elements of our Earth's crust: rocks, soils and minerals. They learn how we categorize rocks, soils and minerals and how they are literally the foundation for our civilization. Students also explore how engineers use rocks, soils and minerals to create the buildings, roads, vehicles, electronics, chemicals, and other objects we use to enhance our lives.
An engineering and design lesson for middle school (our 7th grade standards).
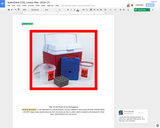
In the aftermath of a natural disaster, can you engineer a device that will keep medicine within a 40-60°F range using natural resources from the biome you live in, and/or debris created by the disaster for three days, until the Red Cross can arrive?
You are a team of relief workers in __________________after a major earthquake/tsunami has occurred. Your team lead as just told you about a young women with diabetes has been injured and needs insulin to be delivered __________ miles away (no open roads). Your team will need to research, design, and build a portable device to keep the insulin between _____ and ______ °(F/C) for _____ days. Once you return you will present the effectiveness of your device to your lead and a team other relief workers showing your both your design/device and explaining the process.
Students learn about the structure of the earth and how an earthquake happens. In one activity, students make a model of the earth including all of its layers. In a teacher-led demonstration, students learn about continental drift. In another activity, students create models demonstrating the different types of faults.

Ground shaking is the primary cause of earthquake damage to man-made structures. This exercise combines three related activities on the topic of shaking-induced ground instability: a ground shaking amplification demonstration, a seismic landslides demonstration, and a liquefaction experiment. The amplitude of ground shaking is affected by the type of near-surface rocks and soil. Earthquake ground shaking can cause even gently sloping areas to slide when those same areas would be stable under normal conditions. Liquefaction is a phenomenon where water-saturated sand and silt take on the characteristics of a dense liquid during the intense ground shaking of an earthquake and deform. Includes Alaska and San Francisco examples.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

Students learn how engineers construct buildings to withstand damage from earthquakes by building their own structures with toothpicks and marshmallows. Students test how earthquake-proof their buildings are by testing them on an earthquake simulated in a pan of Jell-O(TM).