Rectangle and its properties. (Coordinate Geometry)
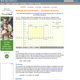
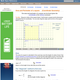
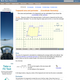
(View Complete Item Description)An interactive applet and associated web page showing how to find the area and perimeter of a rectangle from the coordinates of its vertices. The rectangle can be either parallel to the axes or rotated. The grid and coordinates can be turned on and off. The area and perimeter calculation can be turned off to permit class exercises and then turned back on the verify the answers. The applet can be printed as it appears on the screen to make handouts. The web page has a full description of the method for determining area and perimeter, a worked example and has links to other pages relating to coordinate geometry. Applet can be enlarged to full screen size for use with a classroom projector. This resource is a component of the Math Open Reference Interactive Geometry textbook project at http://www.mathopenref.com.
Material Type: Reading, Simulation