(View Complete Item Description)
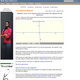
This task provides a construction of the angle bisector of an angle by reducing it to the bisection of an angle to finding the midpoint of a line segment. It is worth observing the symmetry -- for both finding midpoints and bisecting angles, the goal is to cut an object into two equal parts. The conclusion of this task is that they are, in a sense, of exactly equivalent difficulty -- bisecting a segment allows us to bisect and angle (part a) and, conversely, bisecting an angle allows us to bisect a segment (part b). In addition to seeing how these two constructions are related, the task also provides an opportunity for students to use two different triangle congruence criteria: SSS and SAS.
Material Type:
Activity/Lab
Author:
Illustrative Mathematics