National Center for Systemic Improvement – Helping states transform systems to improve outcomes for infants, toddlers, children, and youth with disabilities
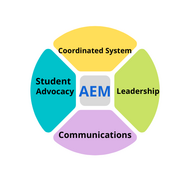
(View Complete Item Description)The Need for a National Center for Systemic Improvement State education agencies play a key role in policy development and implementation, striving to support the field in meeting the needs of students with disabilities and their families. To succeed, they turn to trusted partners to strengthen capacity to lead systems change that improves both learning conditions and outcomes. NCSI is a critical partner to states in these pursuits, assisting them to both learn about and understand seminal research, as well as translate that research into practice. Paying attention to the systemic functions of data literacy, evidence-based practices, stakeholder engagement, and systems coherence, NCSI helps SEAs to cultivate knowledge and skills that enable them to achieve lasting impact for students.
Material Type: Primary Source