Kindergarten Eureka Math
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Assessment
- Author:
- Liberty Public Schools
- Date Added:
- 04/07/2021

Kindergarten Eureka Math

Solve problems involving the four arithmetic operations with rational numbers.
concepts found in Eureka Math- 1st grade
2nd Grade Eureka Math
Write and/or solve linear equations in one variable.
b. Write and/or solve two-step equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q and r are rational numbers, and interpret the meaning of the solution in the context of the problem.
3rd Grade Eureka Math Resources
4th Grade Eureka Math
Eureka math
Create and evaluate expressions involving variables and whole number exponents.
b. Evaluate expressions at specific values of the variables.
d. Write and evaluate algebraic expressions.

Solve one-step equations
Solve one-step linear equations in one variable involving non-negative rational numbers.
*(guaranteeing only whole numbers)
Find the area of polygons by composing or decomposing the shapes into rectangles or triangles.
The placement of a decimal has an effect on the value of a number.
Use decimal fluency to analyze errors and solve real-world situations.

Student can transfer between fractions, decimals, and percents.
Recognize equivalent forms of rational numbers.

Solve problems involving ratios and rates.
a. Create tables of equivalent ratios, find missing values in the tables and plot the pairs of values on the Cartesian coordinate plane.
b. Solve unit rate problems.
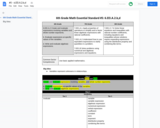
6th Grade Eureka Math Activities, Assessments
7th Grade Eureka Math
Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent expressions.

Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used.

Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable.
b. Solve linear equations and inequalities with rational number coefficients, including equations and inequalities whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and combining like terms. (guarantee limited to equations)
Investigate the difference between linear and nonlinear functions.
Interpret the equation y=mx+b as a defining a linear function, whose parameters are the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b).
Recognize that the graph of a linear function has a constant rate of change.