Video about descriptive vs. inferential statistics.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Author:
- Los Angeles Pacific University
- Date Added:
- 03/31/2021

Video about descriptive vs. inferential statistics.

This task requires students to use the normal distribution as a model for a data distribution. Students must use given means and standard deviations to approximate population percentages. There are several ways (tables, graphing calculators, or statistical software) that students might calculate the required normal percentages. Depending on the method used, answers might vary somewhat from those shown in the solution.
Short Description:
This course blends Introductory Statistics from OpenStax with other OER to offer a first course in statistics intended for students majoring in fields other than mathematics and engineering. This course assumes students have been exposed to intermediate algebra, and it focuses on the applications of statistical knowledge rather than the theory behind it.The foundation of the OpenStax text is Collaborative Statistics, by Barbara Illowsky and Susan Dean. The development choices for this textbook were made with the guidance of many faculty members who are deeply involved in teaching this course. These choices led to innovations in art, terminology, and practical applications, all with a goal of increasing relevance and accessibility for students. We strove to make the discipline meaningful, so that students can draw from it a working knowledge that will enrich their future studies and help them make sense of the world around them.
Word Count: 90414
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

This lesson unit addresses common misconceptions relating to probability of simple and compound events. The lesson will help you assess how well students understand concepts of: Equally likely events; randomness; and sample sizes.

Midterm Exam Review for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Practice Final Exam for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.
This learning video presents an introduction to the Flaws of Averages using three exciting examples: the ''crossing of the river'' example, the ''cookie'' example, and the ''dance class'' example. Averages are often worthwhile representations of a set of data by a single descriptive number. The objective of this module, however, is to simply point out a few pitfalls that could arise if one is not attentive to details when calculating and interpreting averages. The essential prerequisite knowledge for this video lesson is the ability to calculate an average from a set of numbers. During this video lesson, students will learn about three flaws of averages: (1) The average is not always a good description of the actual situation, (2) The function of the average is not always the same as the average of the function, and (3) The average depends on your perspective. To convey these concepts, the students are presented with the three real world examples mentioned above.

This video lesson shows students that math can play a role in understanding how an infectious disease spreads and how it can be controlled. During this lesson, students will see and use both deterministic and probabilistic models and will learn by doing through role-playing exercises. The primary exercises between video segments of this lesson are class-intensive simulation games in which members of the class 'infect' each other under alternative math modeling assumptions about disease progression. Also there is an occasional class discussion and local discussion with nearby classmates.

This task involving amusement park games requires students to calculate probability.
In this dynamic data science game, students try to track down a speck of extremely dangerous radioactive material (the "source"), which has been lost somewhere in the middle of their lab. A special device measures the strength of the radiation and, if it’s positioned correctly over the speck, can be used to collect it for safe disposal. But it's a tiny speck, so they have to give quite precise coordinates. They take measurements to figure out the speck’s location, but must beware: as they take measurements, they're also accumulating radiation exposure. If they get too much, they’ll lose the game and will have to start over. Can they find the source before it’s too late? Using mathematical models, students generate useful strategies for winning the game with data.
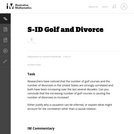
This is a simple task addressing the distinction between correlation and causation. Students are given information indicating a correlation between two variables, and are asked to reason out whether or not a causation can be inferred. The task would be well-suited either as an introduction to this distinction, or as an assessment item.

This problem could be used as an introductory lesson to introduce group comparisons and to engage students in a question they may find amusing and interesting. More generally, the idea of the lesson could be used as a template for a project where students develop a questionnaire, sample students at their school and report on their findings.

The purpose of this task is to assess understanding of how study design dictates whether a conclusion of causation is warranted. This study was observational and not an experiment, which means that it is not possible to reach a cause-and-effect conclusion.

Homework for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Homework for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Homework for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Lecture for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Homework for the course "CS 217 – Probability and Statistics for Computer Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Spring 2019 by Evan Agovino as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

This task is designed as an assessment item. It requires students to use information in a two-way table to calculate a probability and a conditional probability. Although the item is written in multiple choice format, the answer choices could be omitted to create a short-answer task.
This is a task from the Illustrative Mathematics website that is one part of a complete illustration of the standard to which it is aligned. Each task has at least one solution and some commentary that addresses important aspects of the task and its potential use.