- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017


By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify the two major abiotic factors that determine terrestrial biomesRecognize distinguishing characteristics of each of the eight major terrestrial biomes

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Define ecology and the four levels of ecological researchDescribe examples of the ways in which ecology requires the integration of different scientific disciplinesDistinguish between abiotic and biotic components of the environmentRecognize the relationship between abiotic and biotic components of the environment
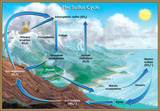
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss the biogeochemical cycles of water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfurExplain how human activities have impacted these cycles and the potential consequences for Earth

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the basic types of ecosystems on EarthExplain the methods that ecologists use to study ecosystem structure and dynamicsIdentify the different methods of ecosystem modelingDifferentiate between food chains and food webs and recognize the importance of each

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how organisms acquire energy in a food web and in associated food chainsExplain how the efficiency of energy transfers between trophic levels affects ecosystem structure and dynamicsDiscuss trophic levels and how ecological pyramids are used to model them

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the basic types of ecosystems on EarthDifferentiate between food chains and food webs and recognize the importance of each


By the end of this section, you will be able to:Compare innate and learned behaviorDiscuss how movement and migration behaviors are a result of natural selectionDiscuss the different ways members of a population communicate with each otherGive examples of how species use energy for mating displays and other courtship behaviorsDifferentiate between various mating systemsDescribe different ways that species learn

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss the predator-prey cycleGive examples of defenses against predation and herbivoryDescribe the competitive exclusion principleGive examples of symbiotic relationships between speciesDescribe community structure and succession
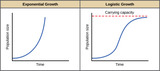
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain the characteristics of and differences between exponential and logistic growth patternsGive examples of exponential and logistic growth in natural populationsDescribe how natural selection and environmental adaptation led to the evolution of particular life history patterns
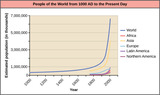
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Discuss how human population growth can be exponentialExplain how humans have expanded the carrying capacity of their habitatRelate population growth and age structure to the level of economic development in different countriesDiscuss the long-term implications of unchecked human population growth


By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how life history patterns are influenced by natural selectionExplain different life history patterns and how different reproductive strategies affect species’ survival
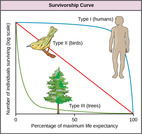
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how ecologists measure population size and densityDescribe three different patterns of population distributionUse life tables to calculate mortality ratesDescribe the three types of survivorship curves and relate them to specific populations
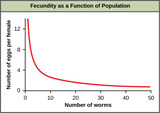
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Give examples of how the carrying capacity of a habitat may changeCompare and contrast density-dependent growth regulation and density-independent growth regulation, giving examplesGive examples of exponential and logistic growth in wild animal populationsDescribe how natural selection and environmental adaptation leads to the evolution of particular life-history patterns
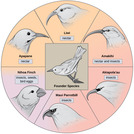
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Define species and describe how species are identified as differentDescribe genetic variables that lead to speciationIdentify prezygotic and postzygotic reproductive barriersExplain allopatric and sympatric speciationDescribe adaptive radiation

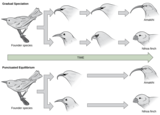
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe pathways of species evolution in hybrid zonesExplain the two major theories on rates of speciation