
Students will learn the basic features of Scratch, a block-based visual prgramming language, and create a simple program using Scratch.
- Subject:
- Computer Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Author:
- Kathy Hay
- Date Added:
- 08/22/2020

Students will learn the basic features of Scratch, a block-based visual prgramming language, and create a simple program using Scratch.

The Shallow and the Deep is a collection of lecture notes that offers an accessible introduction to neural networks and machine learning in general. However, it was clear from the beginning that these notes would not be able to cover this rapidly changing and growing field in its entirety. The focus lies on classical machine learning techniques, with a bias towards classification and regression. Other learning paradigms and many recent developments in, for instance, Deep Learning are not addressed or only briefly touched upon.
Biehl argues that having a solid knowledge of the foundations of the field is essential, especially for anyone who wants to explore the world of machine learning with an ambition that goes beyond the application of some software package to some data set. Therefore, The Shallow and the Deep places emphasis on fundamental concepts and theoretical background. This also involves delving into the history and pre-history of neural networks, where the foundations for most of the recent developments were laid. These notes aim to demystify machine learning and neural networks without losing the appreciation for their impressive power and versatility.
In this video from Science City, Shaundra Bryant Daily, an electrical engineer, describes a software program she developed to help girls reflect on their emotions, and how her two passionsí_í_íŹscience and danceí_í_íŹare connected.
Cost, Accessibility, and Creative Commons Licensing
Short Description:
This book offers authors new perspectives on how to move forward with their work, including how they can make it easily accessible and affordable for their students.
Long Description:
This book offers authors new perspectives on how to move forward with their work, including how they can make it easily accessible and affordable for their students. Written by two librarians, this title provides information on the various file formats for publishing, as well as copyright information.
Word Count: 1504
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

A digital signal processing (DSP) textbook, and other materials, aimed at computer science students. Why one specifically for CS students? DSP has traditionally been taught as part of the electrical engineering curriculum and, as such, is accessible to CS students only to the extent that they have taken its prerequisites. In some engineering schools, that may be the case, but it is often the case that the CS math curriculum lacks some of the expected prerequisites. Moreover, DSP is most often taught as an upper-level EE course, and therefore, practically speaking, inaccessible to most non-EE majors.

Social and Ethical Responsibilities of Computing (SERC), a cross-cutting initiative of the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing, works to train students and facilitate research to assess the broad challenges and opportunities associated with computing, and improve design, policy, implementation, and impacts.
This site is a resource for SERC pedagogical materials developed for use in MIT courses. SERC brings together cross-disciplinary teams of faculty, researchers, and students to develop original pedagogical materials that meet our goal of training students to practice responsible technology development through incorporation of insights and methods from the humanities and social sciences, including an emphasis on social responsibility.
Materials include the MIT Case Studies Series in Social and Ethical Responsibilities of Computing, original Active Learning Projects, and lecture materials that provide students hands-on practice and training in SERC, together with other resources and tools found useful in education at MIT. Original homework assignments and in-class demonstrations are specially created by multidisciplinary teams, to enable instructors to embed SERC-related material into a wide variety of existing courses.
The aim of SERC is to facilitate the development of responsible “habits of mind and action” for those who create and deploy computing technologies, and fostering the creation of technologies in the public interest.
This course presents software engineering concepts and principles in parallel with the software development life cycle. Topics addressed include the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), software modeling using Unified Modeling Language (UML), major phases of SDLC (Software Requirements and Analysis, Software Design, and Software Testing), and project management. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: demonstrate mastery of software engineering knowledge and skills, and professional issues necessary to practice software engineering; discuss principles of software engineering; describe software development life cycle models; learn principles of software modeling through UML as a modeling language; identify major activities and key deliverables in a software development life cycle during software requirements and analysis, software design, and software testing; apply the object-oriented methodology in software engineering to create UML artifacts for software analysis and requirements, software design, and software testing; apply project management concepts in a software engineering environment to manage project, people, and product; participate as an individual and as part of a team to deliver quality software systems. This free course may be completed online at any time. (Computer Science 302)
Software has replaced a diverse array of physical, mechanical, and electronic technologies used before 21st century to create, store, distribute and interact with cultural artifacts. It has become our interface to the world, to others, to our memory and our imagination - a universal language through which the world speaks, and a universal engine on which the world runs. What electricity and combustion engine were to the early 20th century, software is to the early 21st century. Offering the the first theoretical and historical account of software for media authoring and its effects on the practice and the very concept of 'media,' the author of The Language of New Media (2001) develops his own theory for this rapidly-growing, always-changing field.
What was the thinking and motivations of people who in the 1960 and 1970s created concepts and practical techniques that underlie contemporary media software such as Photoshop, Illustrator, Maya, Final Cut and After Effects? How do their interfaces and tools shape the visual aesthetics of contemporary media and design? What happens to the idea of a 'medium' after previously media-specific tools have been simulated and extended in software? Is it still meaningful to talk about different mediums at all? Lev Manovich answers these questions and supports his theoretical arguments by detailed analysis of key media applications such as Photoshop and After Effects, popular web services such as Google Earth, and the projects in motion graphics, interactive environments, graphic design and architecture. Software Takes Command is a must for all practicing designers and media artists and scholars concerned with contemporary media.

This seminar is intended for doctoral students and discusses topics in applied probability. This semester includes a variety of fields, namely statistical physics (local weak convergence and correlation decay), artificial intelligence (belief propagation algorithms), computer science (random K-SAT problem, coloring, average case complexity) and electrical engineering (low density parity check (LDPC) codes).

TED Studies, created in collaboration with Wiley, are curated video collections supplemented by rich educational materials for students, educators and self-guided learners. In Visualizing Data, TED speakers shake up statistics with elegant, dynamic representations that make mountains of data comprehensible and even exciting. Learn how to visualize data and present complicated statistics in elegant and captivating ways. Relevant areas of interest, study and coursework include: information design, demography, statistical literacy, economics, sociology, media studies, linguistics, meteorology and computer science.

Students observe natural selection in action and investigate the underlying mechanism, including random mutation and differential fitness based on environmental characteristics. They do this through use of the free AVIDA-ED digital evolution software application.
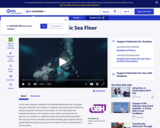
Studying life on the seafloor beneath Antarctica's thick ice is a major challenge for ecologists. Learn about a new device that can reach those icy depths in this video segment adapted from WomenInAntarctica.com.
Syllabus for the course "CSCI 39549: Agile Software Development" delivered at Hunter College in Fall 2018 by Arylee McSweaney and Rebecca Sliter as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Syllabus for the course "CSC 480: Artificial Intelligence" delivered at the College of Staten Island in Fall 2018 by Ernest Battifarano as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Syllabus for the course "CSCI 381/780 - Data Analytics" delivered at Queens College in Spring 2019 by Kumar Ramansenthil as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.
Syllabus for the course "CIS 4400: Data Warehousing for Analytics" delivered at Baruch College in Fall 2018 by Royce Kok as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Syllabus for the course "CIS 356 - Digital Trends and Transformations" delivered at Lehman College in Spring 2019 by Douglas Ng as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Syllabus for CSCI 49378: Introduction to Distributed Systems and Cloud Computing
Syllabus for the course "CSC 59970: Intro to Data Science" delivered at the City College of New York in Fall 2018 by Grant Long as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.

Syllabus for the course "CSCI 380 - Mobile Application and Product Development" delivered at John Jay College in Spring 2019 by Bhargava Chinthirla and Eric Spector as part of the Tech-in-Residence Corps program.