
This video discusses two closely related ideas in economics: scarcity and rivalry.
- Subject:
- Economics
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 07/27/2021

This video discusses two closely related ideas in economics: scarcity and rivalry.
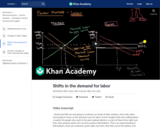
Changes in the demand for labor affect wage rates. Learn why labor demand changes, and the effect of changes in the demand for labor on labor markets.
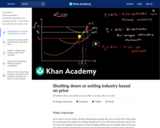
A firm shut's down temporarily when it can't cover its variable cost, but it exits the industry for good when it's economic profits are negative. In this video, learn more about how to use a graph of cost curves to determine when a firm shuts down, enters an industry, or exits an industry.

Short Description:
This book provides detailed foundational tools to assess and evaluate the costs and benefits associated with public or private decision making through a cost-benefit analysis (CBA). This book is targeted at students with preliminary foundations in economics. The content and activities have been developed to support learning in ECON2101 Cost Benefit Analysis offered as a course at UQ.
Word Count: 79884
ISBN: 978-1-74272-370-9
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)
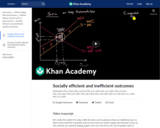
If all costs and benefits are captured by the supply and demand curves, then the market outcome is a quantity where marginal social costs equals marginal social benefit. But what if they don't? In this video, see how markets might produce an inefficient quantity.
Ever wonder why people don’t do everything for themselves? In this video, Professor Art Carden of Samford University explains how specialization and trade create wealth and make us all better off.

A news story interviews a woman who claims that it was difficult for her to find employment because she had children. The story is used to examine the concept of statistical discrimination and whether public policy should be used to discourage statistical discrimination in this case.

Word Count: 10461
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

Word Count: 10295
Included H5P activities: 63
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)
The law of demand states that quantity demanded increases when price decreases, but why? Two reasons why the demand curve slopes downward are the substitution effect and the income effect. The income effect states that when the price of a good decreases, it is as if the buyer of the good's income went up. The substitution effect states that when the price of a good decreases, consumers will substitute away from goods that are relatively more expensive to the cheaper good. Learn about the role of the income effect and the substitution effect on the shape of the demand curve in this video.
When a tax is imposed in a market this is another example of government intervention. In this video, we explore the effect of imposing a tax on the price and quantity in a market. Created by Sal Khan.
An interesting case of taxes and tax incidence is when one of the curves is perfectly elastic. Explore what happens when demand is perfectly elastic in this video. Created by Sal Khan.
The burden of a tax falls most heavily on someone who can't adjust to a price change. That means buyers bear a bigger burden when demand is more inelastic, and sellers bear a bigger burden when supply is more inelastic. Created by Sal Khan.
How to factor in negative externalities through taxation. Created by Sal Khan.

The text of this case is a transcript of a story broadcast on NPR's All Things Considered on January 22, 1996. The story concerns Congressional debate about agricultural programs, particularly the price support program for peanuts. The story includes statements from a member of Congress as well as representatives of peanut growers and peanut processors. The peanut program includes import restrictions, a price floor and peanut growing licenses, and this case describes those and includes statements from peanut growers, processors and consumers.
When a demand curve is linear, calculating consumer surplus becomes relatively simple: calculate the area of a triangle. In this video we walk through calculating consumer surplus. Created by Sal Khan.
The short-run production function describes the relationship between output and inputs when at least one input is fixed, such as out output varies based on the amount of labor used. We can use this production function to find the total product of labor, the marginal product of labor, and the average product of labor.
One of the most practical applications of price elasticity of demand is its relationship to total revenue. A seller who knows the price elasticity of demand for their good can make better decisions about what happens if they raise or lower the price of their good. Explore the relationship between total revenue and elasticity in this video. Created by Sal Khan.
When governments impose restrictions on international trade, this affects the domestic price of the good and reduces total surplus. One such imposition is a tariff (a tax on imported or exported goods and services). See how a tariff impacts price, consumer surplus, producer surplus, tax revenue, and deadweight loss in this video.
The tragedy of the commons occurs when goods are rival but not excludable. In this video, we explore the intuition, and consequences, behind such goods. Created by Sal Khan.