This Carotenoid Biosynthetic Pathway in Peppers (Capsicum annum)
- Subject:
- Biology
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Author:
- Nyra Ahmed
- Date Added:
- 11/29/2021

This Carotenoid Biosynthetic Pathway in Peppers (Capsicum annum)

This video covers the origins and functions of cartilage and collagen.

This multi-term assignment introduces students to local indigenous stories, significant plants and animals of our region and some basic skills in reading animal tracks and signs.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

I designed this activity as a role-playing game to help students understand both the concept of climate modeling and how the climate system works. Students take on the role of a climate system component, examining their personal reactions to climate stimuli and building a future scenario based on their group's reactions. You can implement this teaching collection as part of the Climate of Change InTeGrate Module, Unit 5, or as a stand-alone activity.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

In this activity, students consider how several communities are adapting to climate change-related problems including drought's impacts on agriculture, loss of assets due to climate-related hazards, freshwater availability, and extreme heat waves. They will read brief case studies about agro-forestry, insurance strategies, the "Room for the River" program in the Netherlands, water storage from retreating glaciers, and city planning for heat waves. Based on these examples and knowledge of their own community, they will suggest possible adaptation strategies that will be most beneficial to their area.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

This ocean activity is used to help students analyze different solutions to a real-world case study of the problem of using various coastal stabilization structures. It is intended to be used as a small group activity (3-5 students in each group) following a short introductory lecture about coastal processes (especially longshore drift) and the different types of coastal stabilization structures (jetties, groins, and breakwaters). At the end of the activity, successful students will be able to critically evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of various types of coastal stabilization structures.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)
This is a 'citizen science' research project where students to apply their knowledge of landslide processes in an investigation of the natural and anthropogenic causes of a real-world landslide catastrophe. Students produce a 'magazine' article discussing the Zhouqu, China, August 8, 2010 landslide catastrophe.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

This case represents various agendas, hidden and otherwise, that can come into play during environmental remediation.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

After exploring the “Case of the Disappearing Log,” students will probably never look at a log the same way again. In this activity, students assume the roles of detectives faced with a nature mystery. First, they explore a decomposing log and look for evidence of how the log is changing. They make possible explanations for what might be causing log to disappear. Students then learn about common “suspects”—organisms that decompose wood—and the signature evidence they each leave behind. Students use a Disappearing Log Key to identify which organisms might have left behind which evidence, and use this information to make explanations about what has happened to the log since it was a tree. Finally, students learn that the log isn’t really disappearing, it’s turning into the invisible gases that are part of the cycling of matter in all ecosystems.
Are cell phones really safe for humans to use frequently? In this mock trial lesson, students will use claim, evidence, and reasoning to construct a scientific argument on the safety of the electromagnetic waves involved in cell phone technology. During the lesson process, students will hold a "trial" and each individual student will construct their own written "verdict" based on the evidence presented at the mock trial. This lesson results from the ALEX Resource Gap Project.
In this project, students take on the role of medical students. After being given information about the patient and her environment, they will create a patient treatment plan. Students must use their knowledge of osmosis and how molecules move across cell membranes in order to formulate a treatment plan.
This powerpoint is a short approx. 5 min interactive that demonstrates the purpose and use of the catalase test. I like to share the short and simple powerpoint interactves in addition to videos that demonstrate the process with the students prior to performing the test in the laboratory setting.

Students use phylogenetic analysis to identify farmed Atlantic salmon mislabeled as wild Pacific salmon by local stores and suppliers.
This project allows students to apply molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA sequencing to a real-
world issue.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)

This lesson is a self contained lesson on DNA structure. It will keep the students busy for days and days and even a week or more. There is no associated lecture. It requires no knowledge of DNA or biology or anything. The learning objective is the structure of DNA and nothing more.DNA in cells is elegant in its simplicity. Catch your breath DNA is elegant in its simplicity. Both are made of four things and both can only go together in one way.The core of this cool lesson plan is a paper template. The students will be coloring the bases and cutting them out. They can only go together one way and the students will see that.The paper templates are made on an ordinary copy machine and the template is included in the literature. The templates are copied front and back with a front and back template. But it is not great trick. The download includes all information and there is a video for the teacher and a video for the kids.The lesson plan is suitable for all students, from 4th grade up. It would be suitable for college as well.The documentation can be found here https://app.box.com/s/hlhung3gz5heqmno82yc0xwfs7zl2puhIt references the videos. But the videos is here:https://youtu.be/1BiTYfTpTu4Licensed under Creative Commons ...mrphysh

Students start this exercise using topographic maps of an area recently visited on a field trip to calculate and consider stream gradient of a major river south of Buffalo, NY. The activity then changes gears to have students work with discharge measurements from this stream. They use these measurements to plot and evaluate a few hydrographs which are used to compare how discharge in this stream can be used to consider how much precipitation was received in a certain year. In this lab, students practice mathematically calculating geomorphic properties of a stream, plotting data, and comparing topographic maps to what they observed on the recent field trip.
Designed for a geomorphology course
Uses online and/or real-time data
Addresses student fear of quantitative aspect and/or inadequate quantitative skills
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)
A ~48 page collection of worksheets and review questions for a 300-level Cell Biology Course.

The goal of this course is to teach both the fundamentals of nuclear cell biology as well as the methodological and experimental approaches upon which they are based. Lectures and class discussions will cover the background and fundamental findings in a particular area of nuclear cell biology. The assigned readings will provide concrete examples of the experimental approaches and logic used to establish these findings. Some examples of topics include genome and systems biology, transcription, and gene expression.

The document contains questions to help students practice Cell Biology Concepts. Most of these exercises were short in-class activities, where students would work on these problems for 10-15 min of class. The document also contains a few sets of multiple choice review questions for students to practice concepts on their own.
In this lesson, the students look at the components of cells and their functions. The lesson focuses on the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Each part of the cell performs a specific function that is vital for the cell's survival. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that are very important to engineers. Engineers can use bacteria to break down toxic materials in a process called bioremediation, and they can also kill or disable harmful bacteria through disinfection.
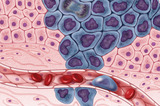
The human body is composed of trillions of cells. Each cell has a life cycle, in the same way that all living things do. In this seminar you will explore and reflect on how eukaryotic cells (that is, cells with a nucleus) reproduce and make copies of themselves.Sometimes there can be mistakes in the copying process, which can lead to cancer. Part of this lesson will show how cancers can happen.Additionally, you will be challenged to create a model of the process to demonstrate your learning of this topic.